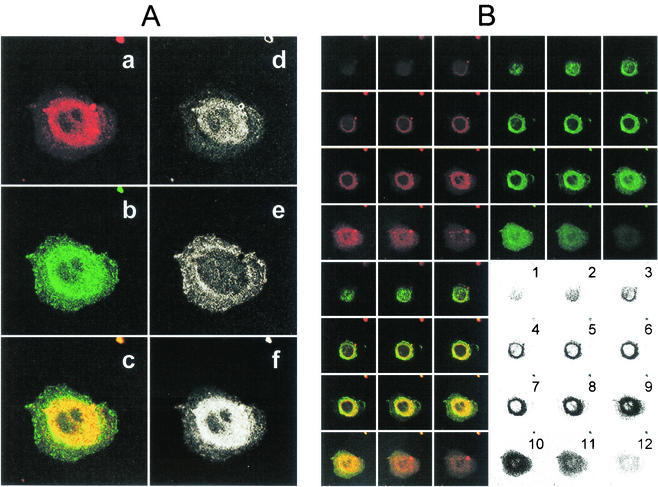
FIG. 7.
Colocalization of dye-labeled HCV-SP and ASGP-R GFP-hH1 in the perinuclear area. HepG2 cells expressing a fusion protein between GFP and ASGP-R hH1 subunit (GFP-hH1-HepG2 cells) were seeded into sterile glass eight-chamber slides 1 day before the assay. HCV-SP was dye (CM-DiI) labeled and purified as described in Materials and Methods. GFP-hH1-HepG2 cells were incubated with 10 μg of CM- DiI-labeled HCV-SP/ml for 60 min at 37°C; the cells were then rinsed and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and the slides were mounted with DAPI-antifade system and kept in the dark at 4°C until they were analyzed by LSCM in both green (GFP) and red (CM-DiI) wavelength channels. (A) Colocalization pattern in a confocal horizontal section of a single cell. In the left column are shown the signals obtained in red (a) and green (b) wavelength channels, and superimposition of a + b signals (c). In the right column, patterns of red (d), green (e), and yellow (f) pixels can be detected in the superimposition picture (c). Most pixels in the perinuclear area are yellow (i.e., green plus red = colocalization). (B) Serial horizontal sections of the same cell (from top to bottom = numbers 1 to 12). Sections were obtained in both green and red wavelength channels (top panels) and superimposed (bottom left panel); areas displaying colocalization are shown in the bottom right panel. A threshold was applied to keep only the most significant pixels; darkness increases with the intensity of the colocalized signals.