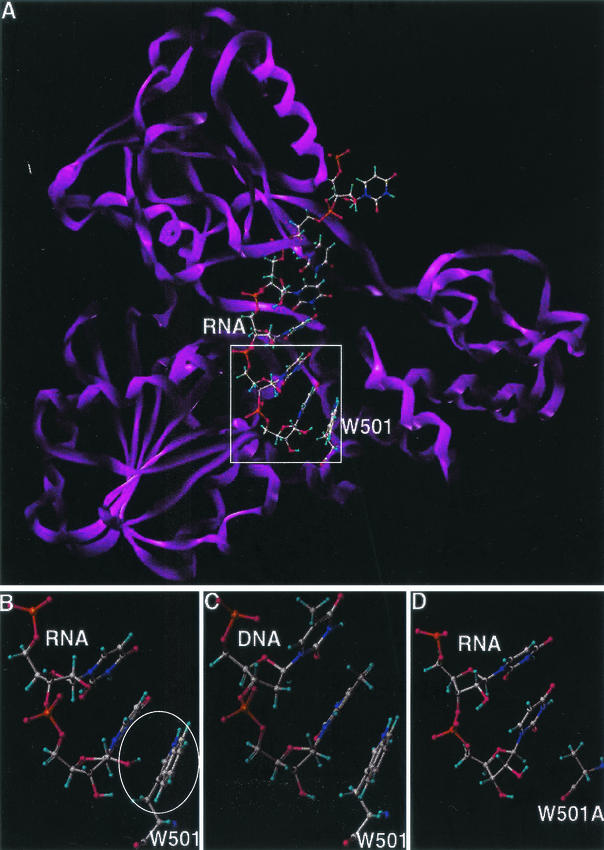
FIG. 7.
Molecular modeling of wild-type and mutant HCV helicases. Carbon is represented in grey, oxygen in red, hydrogen in light blue, nitrogen in indigo, and phosphorus in orange. (A) Wild-type HCV helicase domain complexed with ssRNA U8. The protein is depicted as a ribbon structure (violet); the RNA and W501 residue of the helicase are depicted as a ball-and-stick model. (B) Interaction between the 2′OH of U8 base in ssRNA (top) and the aromatic ring of W501 in the wild-type helicase (bottom). The putative π-facial hydrogen bond is encircled. (C) Lack of the π-facial hydrogen bond interaction between the ssDNA (top) and W501 in the wild-type helicase. (D) Lack of the π-facial hydrogen bond interaction between the ssRNA (top) and Ala side residue in the W501A mutant helicase (bottom).