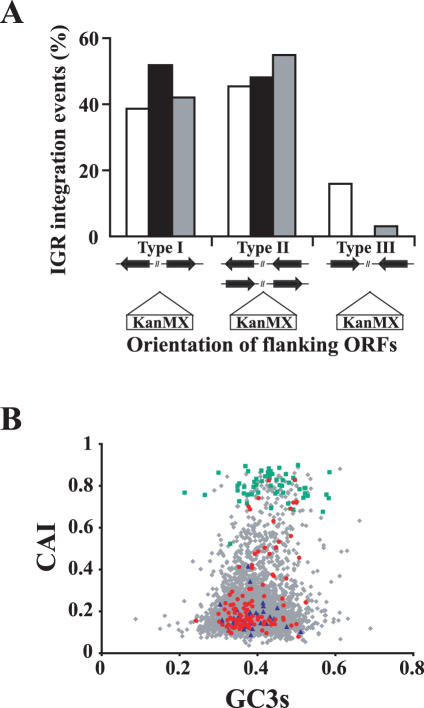
Figure 4.
The genomic target site distribution of IR events is similar in the wild-type and rad52/rad52 strains and occurred preferentially in promoter regions independently of transcriptional activity. (A) IGRs are located either between the 5′ ends of two genes, between the 5′ and the 3′ ends of two similar oriented genes or between the 3′ ends of two opposite oriented genes (type I, type II and type III, respectively). The K.lactis genome wide size of type I, II and III IGRs was calculated by analyzing a random 100 kb DNA segment from each chromosome. The sum of the length of each type of IGR was divided by the total length of all IGR types (298 IGRs analyzed). These values (white bars) thus represent the theoretical fraction each type of IGR occupies in the genome. The SacII-linearized pFA6a-KANMX was transformed into the wild-type CK213-4c strain (black bars) and in the homozygous rad52/rad52 mutant PMY2 strain (grey bars). The genomic target sites of IR were determined as described in Materials and Methods. The percent of type I, II and III IGR insertions with respect to the total number of IGR insertions in each strain was compared to the theoretical expected genome wide value. (B) The CAI values of the genes in which pFA6a-KANMX had integrated in CK213-4c strain within the ORF (blue) and in their 5′-promoter region (red) are shown together with CAI values of all K.lactis protein coding genes (grey) and ribosomal protein genes (green). CAI, codon adaptation index; GC3, the third codon position GC content.