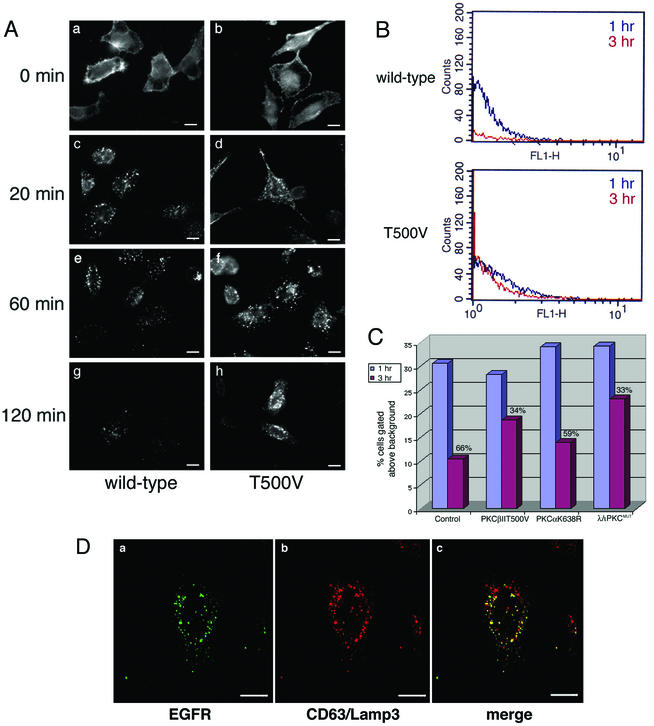
FIG. 6.
EGFR is less efficiently degraded in cells expressing PKCβII T500V. (A) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with the wild-type or kinase-dead (T500V) PKCβII plasmid for 16 h. Cells were then serum starved for 24 h at 37°C. EGF was bound at 4°C for 60 min, and cells were washed and then incubated at 37°C for the indicated times. EGFR was detected by indirect immunofluorescence using an anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody. Bars = 8 μm. (B) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with the PKCβII T500V plasmid for 16 h or were mock transfected. Cells were serum starved, and the EGF uptake assay was performed at 1 h (blue trace) and 3 h (red trace). Cells were prepared for flow cytometry using the monoclonal antibody against the EGFR. (C) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with the kinase-dead (T500V) PKCβII, kinase-dead PKCα (K368R), or dominant-negative PKCλ (λ/ι PKCMUT) plasmid for 16 h or were untransfected. Cells were serum starved, and the EGF uptake assay was performed as described for panel B. Cells were prepared for flow cytometry using the monoclonal antibody against the EGFR. The signal intensity was normalized at the 1 h time point, and the relative amount of EGFR degraded by the 3 h time point is shown as a percentage. (D) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with the PKCβII T500V plasmid for 16 h and then serum starved. EGF uptake was allowed to occur for 120 min. Confocal microscopy studies were used to analyze the expression pattern of the EGFR and late endocytic vesicles. EGFR localization was determined using an anti-EGFR antibody, and late endosomes were localized with an antibody to CD63/Lamp3. Bars = 5 μm.