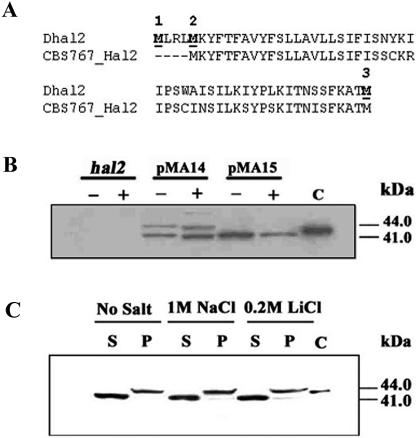
FIG. 2.
Western analysis of Dhal2p expression in S. cerevisiae. (A) Comparison of the N-terminal region of Dhal2p of our clone (Dhal2) with the homologous sequence from D. hansenii strain CBS767 (CBS767_Hal2). Potential initiator methionine residues are numbered and shown in bold. (B) Immunoblot showing expression of the full-length and the truncated forms of Dhal2p in S. cerevisiae. S. cerevisiae strain RS1051 (hal2) or RS1051 carrying plasmid pMA14 (full-length DHAL2) or pMA15 (truncated DHAL2) were grown without (−) or with (+) 1 M NaCl, and total protein extracts from these cultures were made as described in Materials and Methods. Total protein extracts (20 μg) were subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with anti-Dhal2p antibody. In lane C, the purified recombinant truncated Dhal2p was loaded as control. (C) Immunoblot showing localization of Dhal2p in S. cerevisiae. S. cerevisiae strain RS1051 carrying plasmid pMA14 was grown with or without salt as indicated. Cytosolic (S) and membrane (P) fractions from these cultures were made as described in Materials and Methods. A total of 20 μg of protein from each fraction was subjected to immunoblot analysis using anti-Dhal2p antibody. Purified recombinant truncated Dhal2p was loaded as control in lane C. The immunoblot shown is representative of three different experiments.