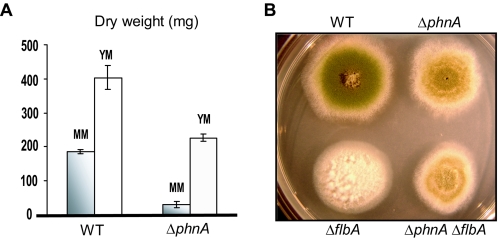
FIG. 2.
PhnA functions in FlbA-controlled vegetative growth signaling pathway. (A) Dry weights of ΔphnA mutant (TJAP3) and wild-type (WT; RJA56.25) strains grown in liquid MM and YM for 24 h (averages of triplicate cultures/measurements with standard error bars). (B) Deletion of phnA suppressed the fluffy-autolytic phenotype caused by the ΔflbA mutation. Relevant mutant and wild-type (WT; JAS30) strains were point inoculated onto solid MM and incubated at 37°C for 3 days. While the ΔflbA mutant (RJA5.9) exhibited the fluffy-autolytic phenotype, the ΔphnA ΔflbA mutant (TJAPF36) showed restored asexual sporulation and enhanced Hülle cell formation and was indistinguishable from the ΔphnA mutant (TJAP3).