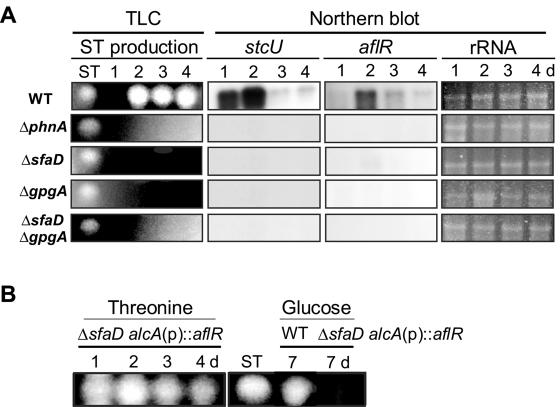
FIG. 5.
Requirement of PhnA, SfaD, and GpgA in ST biosynthesis. (A) Results of TLC and Northern blot analyses of the wild type (WT; FGSC26) and the mutants for ST biosynthesis. Conidia were inoculated in 2 ml of liquid CM and incubated for 1 to 4 days. Numbers indicate the times (days) of incubation. While the WT began to produce ST at 2 days, the ΔphnA (TJAP3), ΔsfaD (RSRB1.15), ΔgpgA (RJAG19.9), and ΔsfaD ΔgpgA (RJA55.4) mutants did not produce detectable levels of ST until 4 days. Moreover, no aflR or stcU mRNA accumulation was clearly detectable in the mutants. The ST standard is indicated. Equal loading of total RNAs was evaluated by ethidium bromide staining of rRNA. (B) The WT (FGSC26) and ΔsfaD alcAp::aflR (RSRAB.4 and RSRAB.1) and ΔsfaD (RSRB1.15; not shown but did not produce ST under any conditions) mutant strains were grown in 2 ml of liquid CM with 2% glucose for 24 h, and then the medium was replaced with liquid CM with threonine or glucose for 1 to 4 days (up to 7 days for glucose-CM). Under noninducing conditions (glucose), only the WT produced ST (only results for 7 days are shown). Note that aflR overexpression in threonine-CM restored ST production in the ΔsfaD mutant.