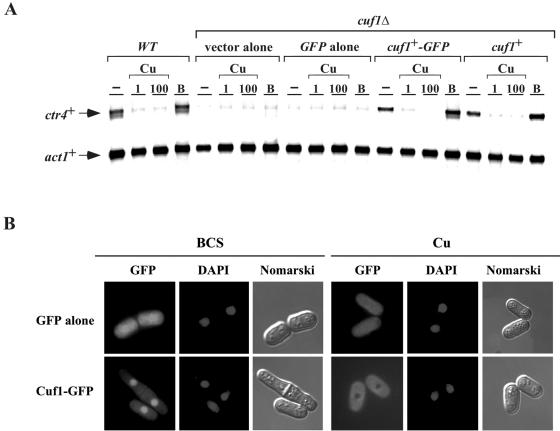
FIG. 5.
Effect of copper on the subcellular localization of a functional Cuf1-GFP fusion protein. (A) An S. pombe strain bearing a disrupted cuf1Δ allele was transformed with an empty vector (vector alone), GFP alone, a functional cuf1+-GFP allele, or a wild-type (WT) cuf1+ allele. Total RNA from control (−), CuSO4 (1 and 100 μM), or BCS (B) (100 μM) cultures was isolated. Shown is a representative RNase protection assay of ctr4+ and act1+ mRNA steady-state levels. Wild-type strain FY435 (cuf1+) was used as a control. (B) Localization of a functional Cuf1-GFP fusion protein in S. pombe. Cells expressing the Cuf1-GFP fusion protein were grown to mid-logarithmic phase and then treated with either BCS (100 μM) or CuSO4 (Cu) (100 μM) for 4 h (GFP). Cells with green fluorescent proteins were treated with DAPI for nuclear DNA staining (DAPI). Nomarski optics was used to examine cell morphology (Nomarski). Cells transformed with GFP alone distributed throughout the cells (cytosol and nucleus) are shown as control.