Figure 3.
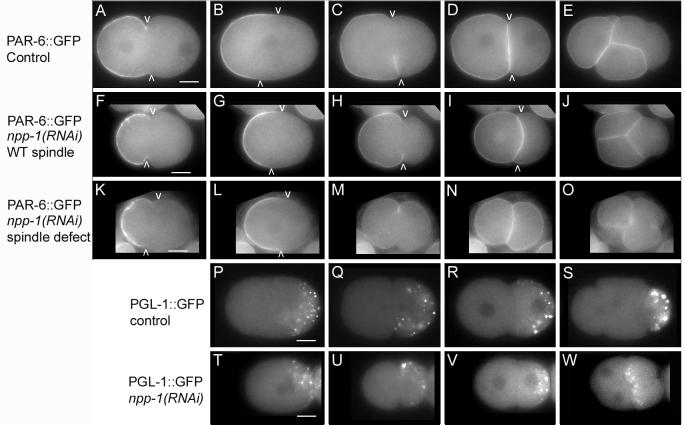
npp-1(RNAi) causes localization defects of PAR-6::GFP and segregation defects of PGL-1::GFP. A-O: Photomicrographs of wild-type embryos (A-E) and npp-1(RNAi) (F-O) embryos expressing PAR-6::GFP. Arrowheads mark the posterior boundary of cortical PAR-6::GFP. F-J: PAR-6::GFP is similar to wild type in an npp-1(RNAi) embryo with normal spindle orientation. K-O PAR-6::GFP is mislocalized at cytokinesis and in the two cell stage in an npp-1(RNAi) embryo with abnormal spindle orientation. P-W: Micrographs of PGL-1::GFP distribution in control embryos (P-S) and npp-1(RNAi) embryos (T-W) at similar time points. PGL-1::GFP initially localizes properly in P0 and P1 in npp-1 (RNAi) embryos (T-V). Subsequently, PGL-1::GFP is improperly segregated to both EMS and P2 in npp-1(RNAi) embryos (W). Bar represents 10 microns.
