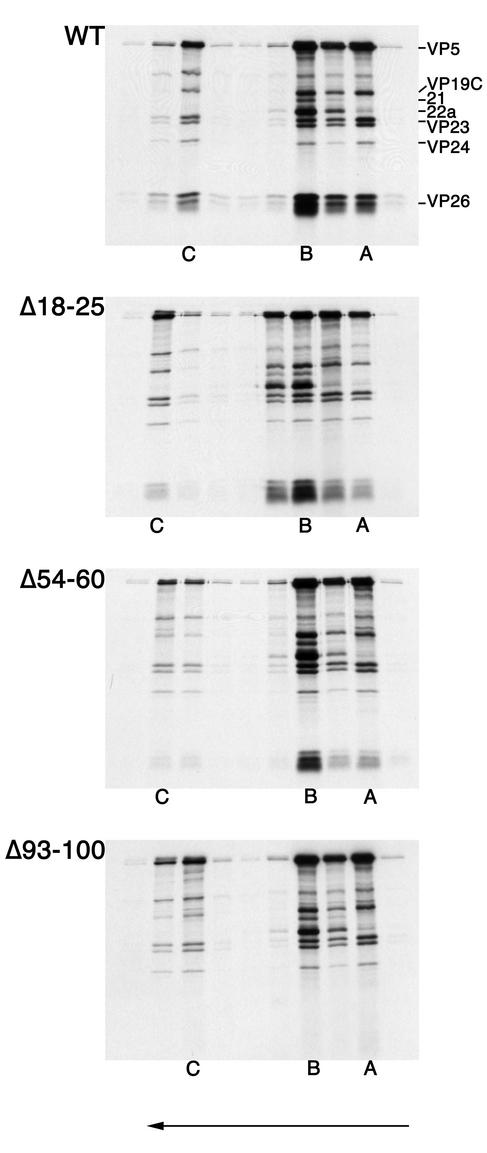
FIG. 6.
Deletion of the conserved residues in the C terminus of VP26 eliminates capsid binding. All three nuclear capsids were isolated and purified from lysates of KΔ26Z-infected cells. The infected cells were metabolically labeled with [35S]methionine. The capsids were mixed with radiolabeled translation products of wild-type VP26 or the three in-frame deletion mutants. Following incubation of capsids and in vitro-translated protein, the mixture was sedimented through 20 to 50% sucrose gradients. The fractions collected were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (17% acrylamide). The gels were processed as described in Materials and Methods and dried prior to autoradiography, and the autoradiograph obtained is shown in the figure. The direction of sedimentation was from right to left (indicated by the arrow at the bottom of the figure). The positions at which A, B, and Ccapsids sedimented are indicated at the bottom of the panels. The positions of VP5, VP19C, 21, 22a, VP23, VP24, and VP26 are indicated on the left of the top panel.