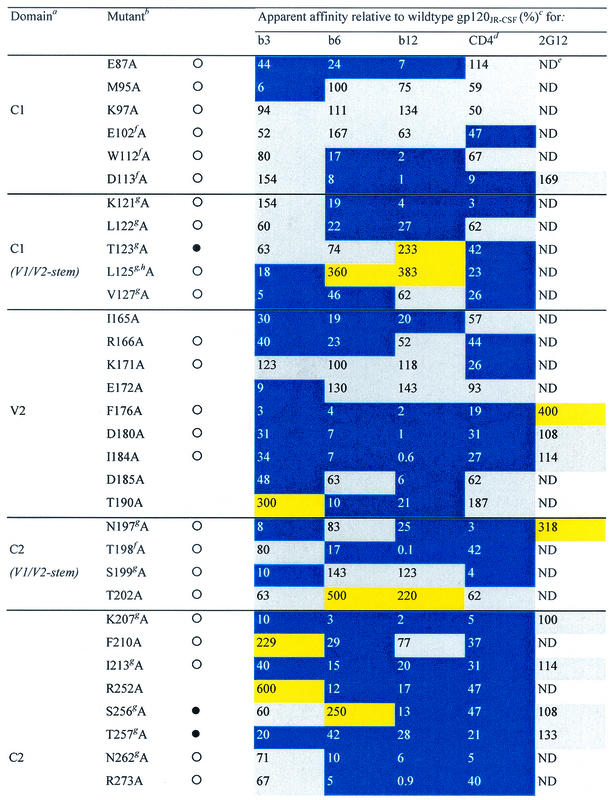
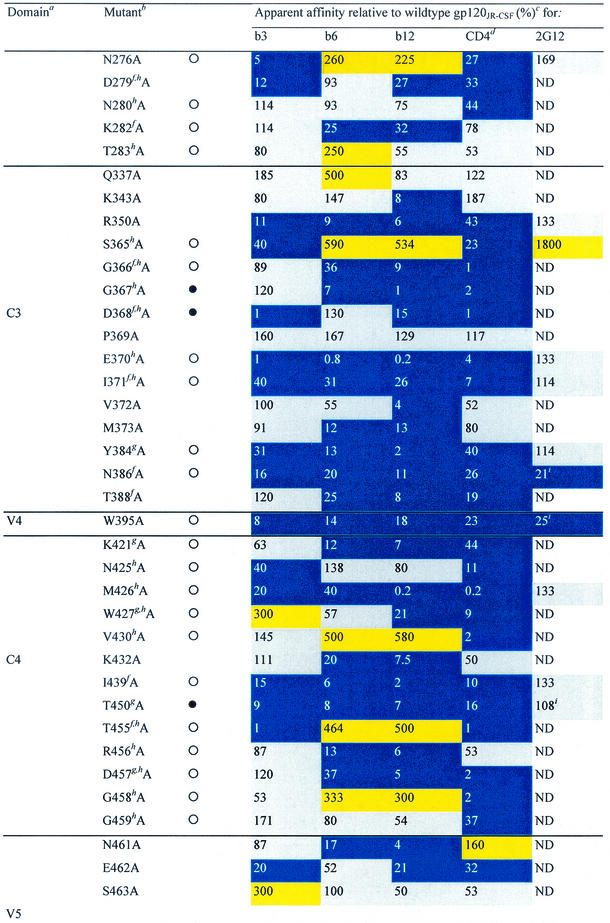
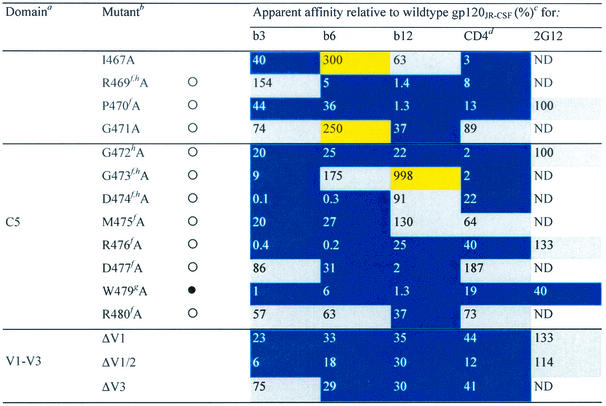
TABLE 1.
Alanine and variable loop deletion mutants generated in this study and their binding to MAbs and CD4
gp120 domain. C, constant domain; V, variable loop. Amino acid numbering is relative to that of HIV-1HxB2, where 1 is the initial methionine (26). Δ, amino acid deletions: ΔV1, amino acids 134 to 154; ΔV1/V2, amino acids 134 to 154 and 160 to 193; and ΔV3, amino acids 303 to 324. White circles indicate that an amino acid is identical among 51 to 98% of all HIV-1 isolates. Black circles indicate that an amino acid is identical among 99 to 100% of all HIV-1 isolates. Amino acid identity was determined from a sequence alignment of HIV-1 isolates listed in the HIV sequence database at http://hiv-web.lanl.gov/content/hiv-db/mainpage.html. Apparent affinities were calculated as the antibody concentration at half-maximal binding. Apparent affinities relative to those for wild-type gp120 were calculated with the formula (apparent affinity for the wild type/apparent affinity for the mutant) × 100. The color scheme is the same as that in Fig. 3; substitutions which resulted in an apparent affinity of <50% relative to that for the wild type are colored blue, those which resulted in an apparent affinity of 50 to 200% relative to that for the wild type are colored grey, and those that resulted in an apparent affinity of >200% relative to that for the wild type are colored yellow. CD4-IgG2 was used as a surrogate for CD4 in this study. ND, not determined. Amino acid residues conserved among all HIV-1 isolates. Amino acid conservation is defined as in reference 30: single amino acid changes are allowed, as are larger substitutions, as long as the character of the side chain is maintained (e.g., Lys to Arg or Phe to Leu). Amino acid residues conserved among all primate immunodeficiency viruses. CD4 contact residues (as determined from the crystal structure of the gp120-CD4-17b complex by Kwong et al. [30]). Data were derived from reference 62.