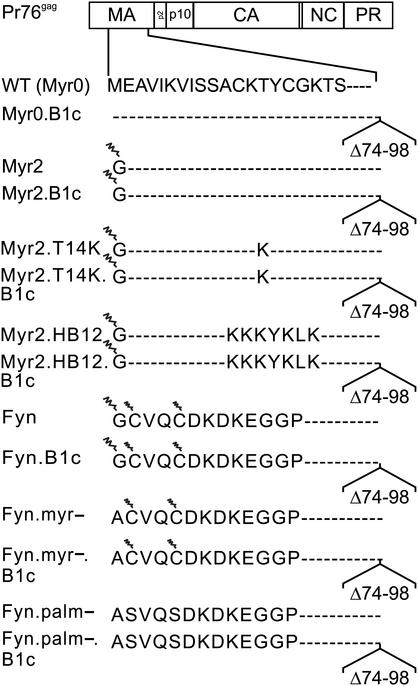
FIG. 1.
Mutants of the RSV M domain. The arrangement of the cleavage products produced from the wild-type [WT (Myr0)] Gag polyprotein is depicted at the top. The E2G substitution, termed Myr2, allows cotranslational addition of myristic acid (depicted as a zigzag line) to the N terminus of Gag. Mutations Myr2.T14K and Myr2.HB12 insert basic residues from the M domain of HIV either individually or within a cluster in the context of the myristoylated N terminus. The Fyn substitution replaces the first 10 amino acids of the RSV M domain with that of Fyn; a G2A change within this sequence, termed Fyn.myr−, prevents both the myristoylation of Fyn at position 2 and the reversible palmitoylation (indicated by the smaller zigzag line) at positions 3 and 6. The Fyn.palm− mutation substitutes alanines for cysteines that are the sites of Fyn palmitoylation. The deletion B1c removes the fourth alpha-helix of the M domain (amino acids 73 to 86) and extends through residue 98.