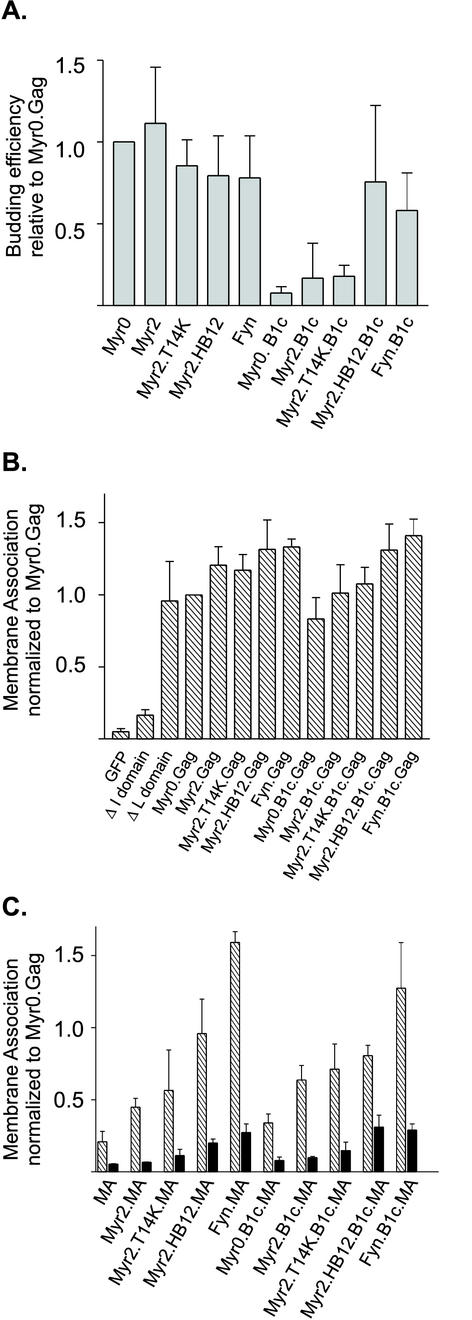
FIG. 2.
Particle assembly and membrane association of the wild-type and mutant Gag.GFP and MA.GFP fusion proteins. (A) Budding efficiency. To determine the ability of each Gag derivative to assemble virus-like particles, QT6 cells transfected with indicated Gag.GFP derivatives were labeled for 2.5 h with l-[35S]methionine, lysed, and immunoprecipitated with polyclonal serum against RSV. Budding efficiency was calculated by dividing the amount of Gag detected in the extracellular medium by the sum of the Gag protein present in the cell lysate plus that in the medium. Budding for each mutant was normalized to Gag.GFP, which was assigned the value of 1.0. (B) Membrane association of wild-type and mutant Gag.GFP proteins. Transfected QT6 cells were fractionated by hypotonic lysis, and membranes were pelleted by differential centrifugation. Membrane association was determined by quantification of the amount of fluorescence present in the membrane (P100) fraction divided by the amount present in both the membrane and soluble fractions (P100 + S100). (C) Membrane association of wild-type and mutant MA.GFP proteins. Membrane association was determined as explained in the legend to panel B. Black bars represent samples that were pretreated with 0.5% Triton X-100 prior to membrane pelleting. Error bars (A to C) represent the standard deviation of three or more independent experiments.