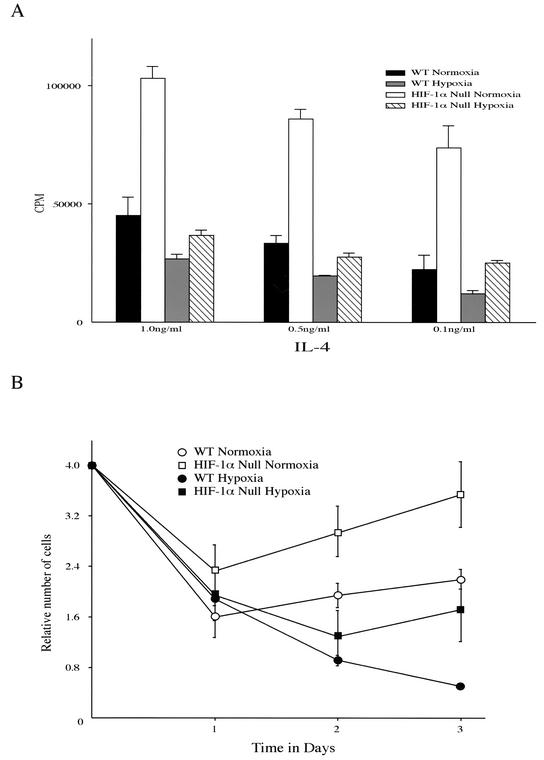
FIG. 3.
Enhanced expansion of HIF-1α null B cells in response to mitogen. (A) Thymidine incorporation upon mitogenic stimulation of isolated B cells under either normoxia or hypoxia. B cells isolated from either HIF-1α null (HIFDFCD19cre) or wild-type (WT) (CD19cre) mice were stimulated with anti-IgM antibody (10 μg/ml) plus IL-4 (1, 0.5, or 0.1 ng/ml) under either normoxia or hypoxia for 48 h. The incubation with [3H]thymidine was performed for the last 12 h. The results shown are the average values for two CD19cre and HIFDFCD19cre mice. Note that B cells in which the HIF-1α gene had been deleted (HIF-1α null B cells) incorporated more thymidine than wild-type cells under either normoxia or hypoxia in response to mitogenic stimulation. (B) Proliferation curves of isolated splenic B cells under normoxia and hypoxia. HIF-1α null B cells show increased growth rates during normoxic and hypoxic culture. Isolated B cells were incubated with anti-IgM antibody (10 μg/ml) plus IL-4 (0.5 ng/ml) under either normoxia or hypoxia for 3 days. Viable cells were counted after staining with trypan blue. The results shown are the average values for two wild-type (WT) (CD19cre) and HIF-1α null (HIFDFCD19cre) mice.