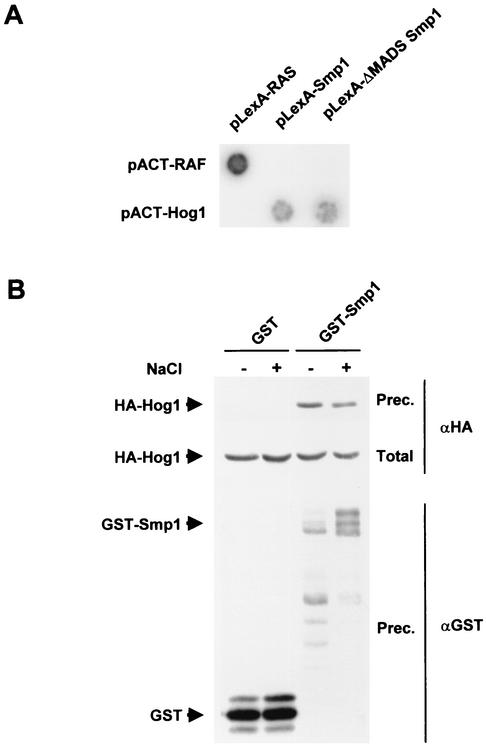
FIG. 3.
In vivo binding of Hog1 to Smp1. (A) Interaction as shown by two-hybrid analysis of Hog1 and Smp1. The wild-type version and a mutant that lacks the MADS and MEF2 domains (ΔMADS Smp1) fused to the LexA DB were expressed with the full-length HOG1 fused to the GAL4 activator domain. A representative filter β-galactosidase assay demonstrating interactions between Hog1 and Smp1 is shown. Proteins encoded by the control plasmids pLexA-RASV12 and pACT-RAF, which are known to interact with each other, are shown for comparison. (B) Smp1 coprecipitates with Hog1. Strain YEN114 (which expresses HA-tagged Hog1 from the wild-type locus) was transformed with a plasmid expressing GST or GST-SMP1 under the PGAL1 promoter. Cells were grown in the presence of galactose, and samples were taken before (−) or 10 min after (+) the addition of NaCl to a final concentration of 0.4 M. GST proteins were affinity purified through a glutathione-Sepharose matrix; the presence of HA-Hog1 in the precipitates was probed by immunoblotting with anti-HA (indicated by αHA at right), and GST-containing proteins (indicated by αGST at right) were detected by using antibodies against GST. Total, <10% of the input protein; Prec., total amount of Hog1 or GST precipitated.