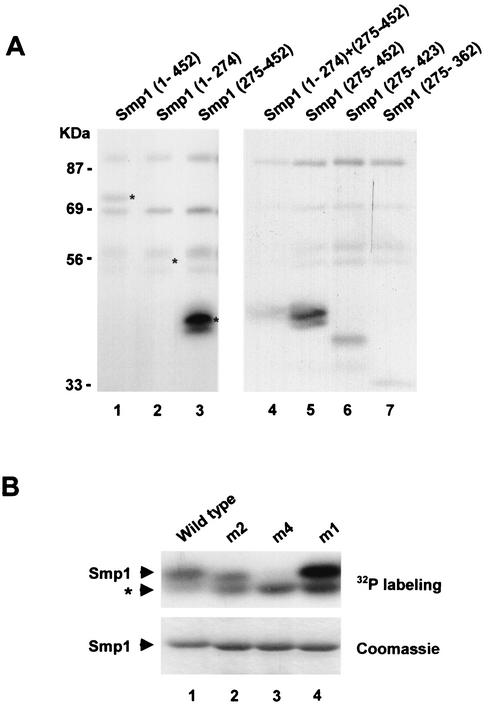
FIG. 4.
Hog1 phosphorylates the C-terminal domain of Smp1. (A) In vitro-activated Hog1 phosphorylates Smp1. Various Smp1 fragments were tested for their ability to be phosphorylated by an in vitro-activated Hog1. The positions of the Smp1 fragments included in the constructs are indicated in parentheses. Recombinant tagged proteins were purified from E. coli and subjected to phosphorylation by activated Hog1 as described in Materials and Methods. Phosphorylated proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and detected by autoradiography. Asterisks indicate the positions of Smp1 proteins detected by Coomassie staining. (B) Mutation of Smp1 Ser348, Ser357, Thr365, and Ser376 to Ala abolishes Hog1 phosphorylation. The wild-type Smp1 fragment (amino acids 275 to 452) and various Smp1 site-directed mutants were tested for Hog1 phosphorylation as described in the legend for panel A. The Smp1 mutants and their corresponding mutations (indicated in parentheses) are as follows: m2 (Ser348 and Ser357 to Ala), m4 (Ser348, Ser357, Thr365, and Ser376 to Ala), and m1 (Thr365 and Ser376 to Ala). After phosphorylation, the proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and phosphorylated proteins were detected by autoradiography (upper panel). GST-tagged Smp1 proteins were detected by Coomassie blue stain (lower panel). The asterisk indicates a contaminant phosphorylation not corresponding to Smp1.