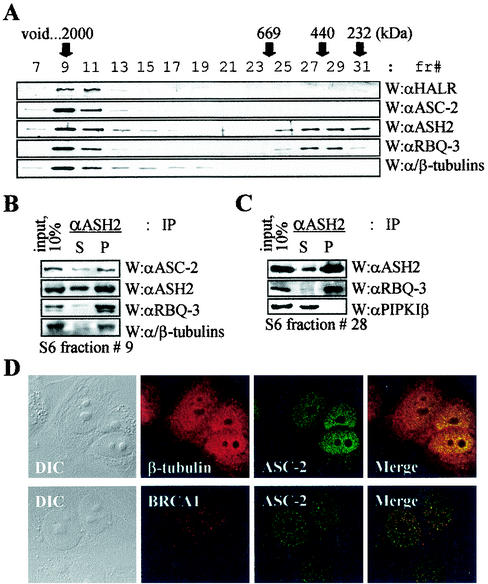
FIG. 3.
α/β-Tubulins in ASCOM. (A) For the size fractionation of ASCOM, HiTrapQ fractions 40 to 44 (shown in Fig. 2A) were loaded onto a Mono S column (HR5/5; Pharmacia). Immunoreactive fractions were pooled, applied to a Superose 6 column (HR10/30; Pharmacia), and analyzed by immunoblotting as indicated. fr#, fraction number; W, Western analysis; αHALR, anti-HALR; αASC-2, anti-ASC-2; αASH2, anti-ASH2; αRBQ-3, anti-RBQ-3. (B and C) Superose 6 fraction 9 (B) or 28 (C) containing ASCOM or a smaller complex of approximately 500 kDa was immunoprecipitated with the indicated antibodies (IP), separated by SDS-4 to 6.5% PAGE, and probed with indicated antibodies (W). S and P indicate supernatant and precipitate, respectively. Ten percent of the total reaction mixture was loaded as input. αPIPKIβ, anti-PIPKIβ. (D) Cells were treated with β-tubulin, BRCA1, and ASC-2 antibodies. Fluorescein isothiocyanate (green)- and tetramethyl rhodamine isothiocyanate (red)-conjugated antibodies were used to detect ASC-2 and β-tubulin/BRCA1, respectively. Note the colocalization of ASC-2 and β-tubulin. Similar results were also obtained with α-tubulin antibody (data not shown). DIC, differential interference contrast.