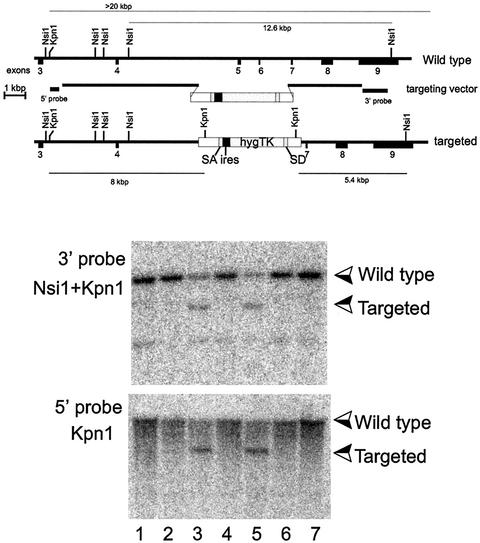
FIG. 1.
Homologous recombination into the sir2α locus. The sequence for sir2α mRNA was inferred from the expressed sequence tag database, and reverse transcription-PCR was used to amplify and clone a cDNA corresponding to exons 3 to 9. This cDNA sequence was confirmed and used to isolate two overlapping genomic clones derived from strain 129/Sv mice. DNA sequencing was used to locate the exons, as shown in the upper panel. The targeting vector was constructed as shown, where the selectable sequence replaces exons 5 and 6, which encode highly conserved regions of the catalytic domain of the SIR2α protein. The selectable sequence consists of splice acceptor (SA) and splice donor (SD) sequences derived from exons 3 and 5 of the mouse Pgk-1 gene (3) surrounding the poliovirus internal ribosome entry site (ires) (35) and the coding region for a gene fused from the hygromycin and herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (TK) genes (30). The targeting vector was linearized and electroporated into the R1 line of ES cells (36), which were subsequently selected for hygromycin resistance. Individual clones were isolated and expanded, and their DNA was analyzed by Southern blotting following digestion with the enzymes shown in the two lower panels. The two clones shown in lanes 3 and 5 had patterns of hybridizing bands that are consistent with homologous recombination having occurred at both the 5′ and 3′ ends of the targeting vector.