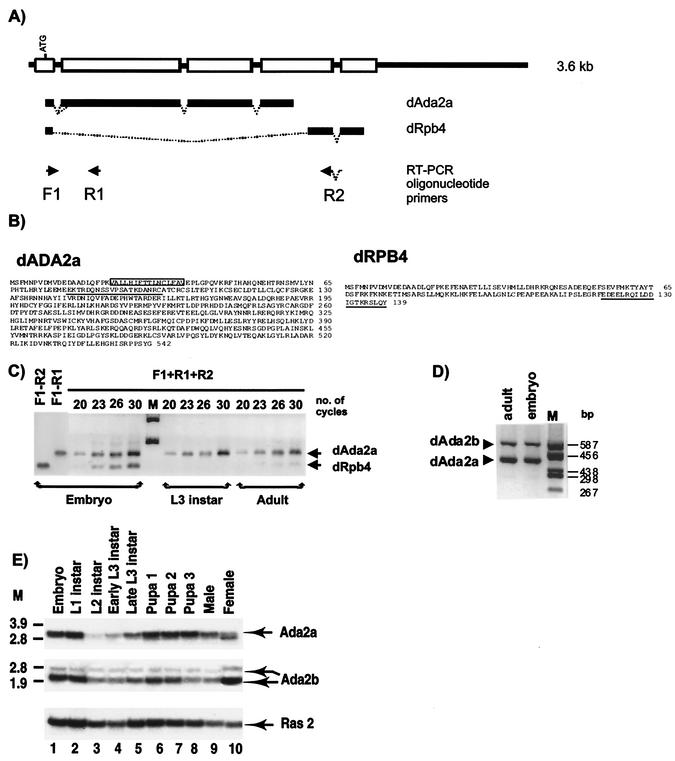
FIG. 1.
The dAda2a/dRpb4 gene encodes two putative transcription factors, dADA2a and dRPB4. (A) Schematic representation of the dAda2a/dRpb4 gene structure. Exons are shown as boxes on the thick line representing the genomic sequence. The common ATG located in the first exon is indicated. The dAda2 and the dRpb4 transcripts produced by alternative splicing are indicated as bold lines under the genomic structure. F1, R1, and R2 show the locations of oligonucleotide primers used for RT-PCR analysis of the dAda2 or dRpb4 mRNA. (B) Deduced amino acid sequences of the Drosophila ADA2a and RPB4 proteins. The 15-amino-acid stretch that is generated by alternative 3′ splice site selection in certain dADA2a isoforms is boxed. The oligopeptides used for immunization to produce specific antibodies against dADA2a and dRPB4 are underlined. (C) RT-PCR analysis of total RNA prepared from Drosophila at different developmental stages, as indicated. The arrows show the dAda2a- and dRpb4-specific PCR products. Aliquots from each PCR amplification reaction were taken at 20, 23, 26, and 30 cycles, resolved on a 1.2% agarose gel, and visualized by ethidium bromide staining. M, molecular weight marker. (D) RT-PCR analysis using total RNA prepared from developmental stages, as indicated above the lanes. The dAda2a and dAda2b PCR products with different sizes are indicated. Aliquots from each PCR amplification reaction were resolved on a 2% agarose gel and visualized by ethidium bromide staining. M, molecular weight marker. (E) Northern blot analysis of dAda2a and dAda2b mRNAs during Drosophila development. cDNA fragments from either dADA2a or dADA2b cDNAs were labeled and hybridized with mRNA samples prepared from the indicated stages of the Oregon R strain. The same blot was also hybridized with the Ras2 probe as a control (53). M, molecular weight marker.