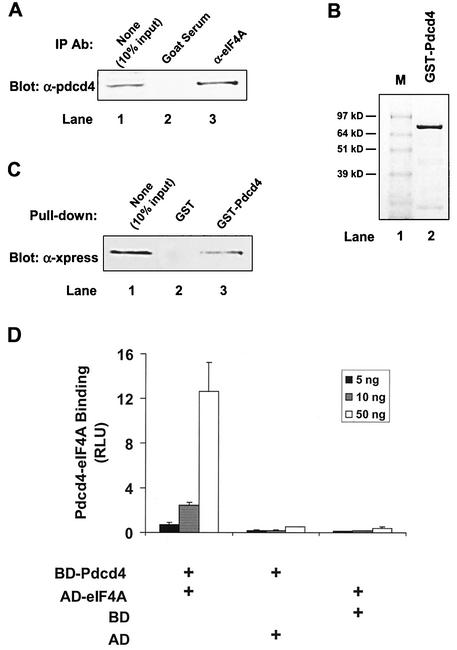
FIG. 1.
Identification of Pdcd4 binding to eIF4A. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation of Pdcd4 with eIF4A. JB6 P+ cell lysates isolated following transient transfection with Pdcd4 expression plasmid were immunoprecipitated (IP) with goat serum (lane 2) or eIF4A antibody (Ab) (lane 3). The immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS-10% PAGE followed by immunoblotting with Pdcd4 antibody. Lane 1 shows one-tenth of the cell lysates. (B) Coomassie blue staining of GST-Pdcd4. One microgram of GST-Pdcd4 expressed in SF-9 cells and purified from a glutathione column as described in Materials and Methods was loaded onto SDS-PAGE (10%) and stained with SimpleBlue (Invitrogen). Lane M, protein molecular size markers. (C) GST pull-down of eIF4A with Pdcd4. JB6 P+ cell lysates isolated following transient transfection with Xpress-tagged eIF4A expression plasmid were pulled down with GST (lane 2) or GST-Pdcd4 (lane 3). The bound proteins were resolved by SDS-10% PAGE followed by immunoblotting with Xpress antibody. Lane 1 shows one-tenth of the cell lysates. (D) Mammalian two-hybrid assay of Pdcd4 binding to eIF4A. Various amounts (5, 10, and 50 ng) of plasmid pCMV-BD-Pdcd4 (or its empty vector, pCMV-DB) and pCMV-AD-eIF4A (or its empty vector, pCMV-AD) along with the Gal4-luciferase reporter gene were cotransfected into JB6 P+ cells. After 48 h, cells were lysed, and the luciferase activity was measured. The luciferase activity from the cells with 5 ng of pCMV-BD-Pdcd4 and 5 ng of pCMV-AD-eIF4A was designated as 1. These experiments were repeated three times, each with five independent transfections, and representative data are shown. Results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. RLU, relative luciferase units.