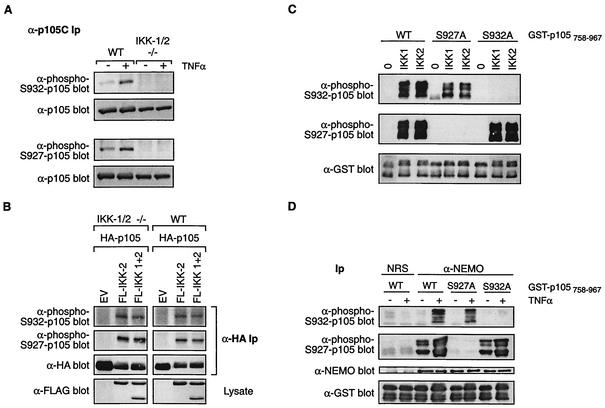
FIG. 4.
The IKK complex directly phosphorylates serine 932 of p105. (A) Wild-type (WT) and IKK1/2-/- (−/−) EFs were pretreated with MG132 for 30 min and then incubated for a further 30 min with TNF-α or control medium. p105 was then immunoprecipitated from cell lysates and Western blotted with the indicated antibodies. Ip, immunoprecipitates. (B) IKK1/2−/− or wild-type EFs were transiently cotransfected with the indicated expression vectors. Cells were treated with MG132 for the last 4 h of a 48-h culture. HA-p105 was isolated from cell lysates by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotted with the antibodies shown. (C) In vitro kinase assays were carried out with baculovirus-produced purified His6-IKK1 or His6-IKK2 (100 ng), using as substrates 5 μg of wild-type or point-mutated GST-p105758-967 protein, as indicated. Phosphorylation was assessed by sequentially immunoblotting with anti-phospho-Ser932 (upper gel) or anti-phospho-Ser927 (middle gel) antibodies. Equal loading of fusion proteins was confirmed by reprobing blots with anti-GST MAb (lower gel). (D) HeLa cells were stimulated for 15 min with TNF-α or left unstimulated. The endogenous IKK complex was isolated from cell lysates by immunoprecipitation with an anti-NEMO antibody. Control immunoprecipitations were carried out with nonimmune rabbit serum (NRS). Phosphorylation was assessed as described for panel C. Blots were probed with anti-NEMO antibody to confirm that equal amounts of IKK complex were immunoprecipitated.