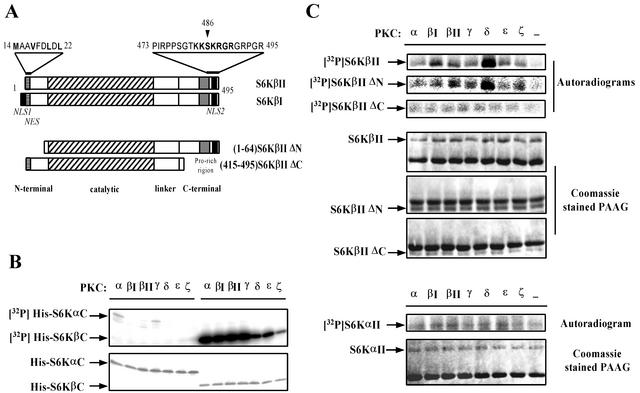
FIG. 1.
S6KβII, but not S6KαII, is phosphorylated at the C terminus by different PKC isoforms in vitro. (A) Schematic representation of S6KβI and S6KβII and their deletion mutants, which lack amino- and carboxyl-terminal sequences. Major domain boundaries are indicated. Structural features are indicated as follows: grey boxes indicate unique proline-rich sequences of S6Kβ; solid black boxes indicate NLSs (NLS1 and NLS2); striped boxes correspond to potential NESs. The N- and C-terminal amino acid sequences, containing NES and NLS, are shown above the diagrams. All recombinant constructs carry an N-terminal EE-tag sequence, and deleted amino acids are indicated. (B) In vitro phosphorylation of bacterially expressed His-S6KαC and His-S6KβC by various PKCs. Affinity-purified His-tagged S6Kα and S6Kβ C-terminal peptides were incubated in the presence of different recombinant PKC isoforms and [γ-32P]ATP. The reaction mixtures were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie. The dried gel was analyzed by autoradiography. (C) In vitro phosphorylation of recombinant full-length S6KαII, S6KβII, and deleted S6KβII mutants by PKCs. HEK 293 cells transiently transfected with wild-type EE-S6KαII, EE-S6KβII, EE-S6KβIIΔN, or EE-S6KβIIΔC were serum starved for 24 h, and recombinant proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-EE-tag antibody. The immunoprecipitates were incubated with [γ-32P]ATP in the absence or presence of different recombinant PKC isoforms. The reaction mixtures were analyzed as described above.