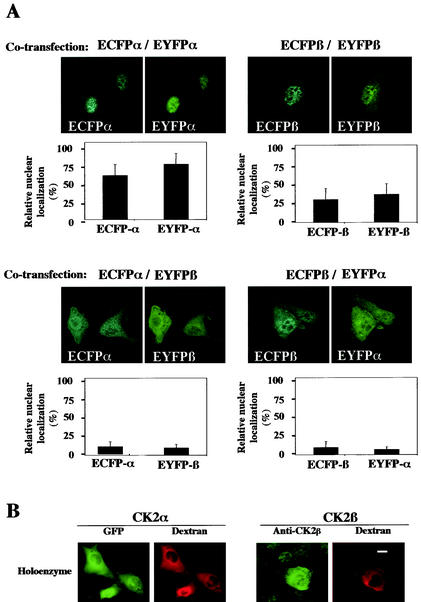
FIG. 4.
Interaction between the CK2 subunits precludes their nuclear import. (A) NIH 3T3 cells were cotransfected with different combinations of the following plasmids: enhanced cyan fluorescent protein (ECFP)-CK2α/enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EYFP)-CK2α, ECFP-CK2β/EYFP-CK2β, ECFP-CK2α/EYFP-CK2β, or ECFP-CK2β/EYFP-CK2α. Sixteen hours after transfection a dual-color imaging analysis was performed. Cotransfected cells (150 to 300) were scored according to whether the level of fluorescence of GFP was higher in the nucleus than in the cytoplasm, and the results were expressed as a percentage of the total number of transfected cells. Error bars, standard deviations. (B) A complex between GFP-CK2α and CK2β (holoenzyme) was recombined in vitro and microinjected into the cytoplasm of NIH 3T3 cells in interphase along with 70-kDa dextran Texas Red. Localization of the GFP CK2α was followed by monitoring GFP fluorescence every 15 s. Images shown are after 10 min. Localization of CK2β was detected by indirect immunofluorescence using anti-CK2β antibodies on cells fixed 10 min after injection. Bar, 10 μm.