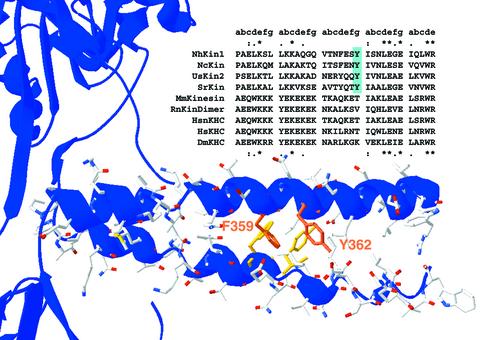
Fig. 1. Primary sequence and structural model of the kinesin neck domain. A sequence alignment of several conventional kinesin neck domains highlights the distinct and conserved sequence patterns of fungal and animal neck regions. The heptad structure of the coiled-coil is indicated above the alignment. In the first and last heptads, homology between fungal and animal kinesins is visible, indicated by asterisks for amino acid identity and dots for similarity. The central heptad of the neck clearly differs in fungi and animals. The Y362, highlighted in blue, is strictly conserved within all fungal kinesins but is not present in animals. In the lower part of the figure, the primary sequence of the NcKin neck is modelled into the crystal structure of the neck coiled-coil from rat conventional kinesin (3KIN). The aromatic residues F359 and Y362 are highlighted. Kinesins from: NcKin, N.crassa; UsKin2, Ustilago maydis; SrKin, S.racemosum; MmKin, Mus musculus; HsnKHC Homo sapiens KHC, neuronal isoform; HsKHC H.sapiens ubiquitous kinesin; DmKHC, Drosophila melanogaster; RnKinDimer, rat kinesin dimer.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.