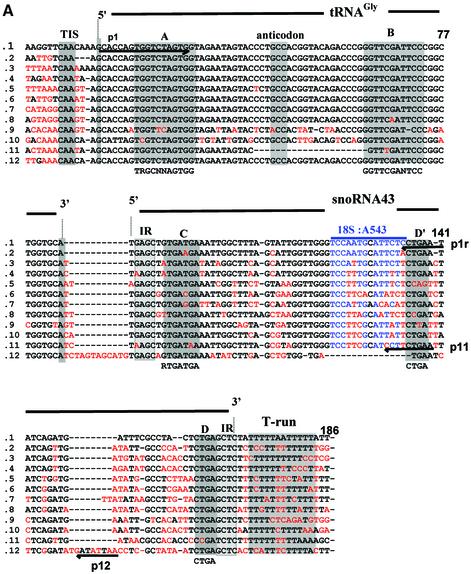
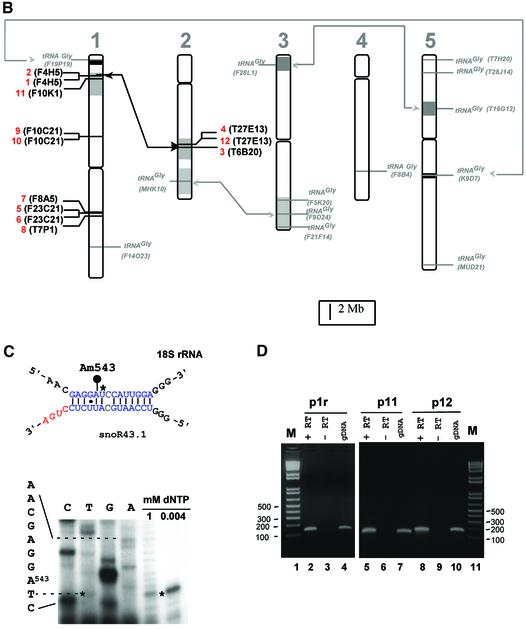
Fig. 1. Genomic organization of the tsnoR43 dicistronic genes. (A) Sequence alignment of the tsnoR43 genes. The tRNAGly sequences are in the Arabidopsis tRNA databanks (see Materials and methods for addresses). SnoRNAs were predicted by SnoScan (Lowe and Eddy, 1999). Divergent nucleotides are in red. Grey boxes indicate functional elements on the tRNA and snoRNA. Consensus sequences for tRNA A and B boxes (Geiduschek and Tocchini-Valentini, 1988) and snoRNA C and D boxes (Bachellerie and Cavaillé, 1998) are indicated below. The blue overline indicates the rRNA antisense element of snoR43.1 targeting 18S:A543 and blue nucleotides display rRNA/snoRNA pairing. IR indicates inverted repeats forming a terminal stem on C/D snoRNAs. The RT–PCR sense primer p1 annealing to the tRNA and the 5′ ends of the reverse primers p1r, p11 and p12 are underlined with arrows. (B) Chromosomal location of tsnoR43 genes. The 12 dicistronic tsnoR43 genes are shown in red. The 13 single tRNAGly genes are shown in grey. The name of the BAC containing these genes is given in parentheses in each case. Lines link isoforms located in large chromosomal duplications shown by the shaded regions (Blanc et al., 2000). (C) The 18S:A543 is 2′-O-methylated in the 18S rRNA. Methylation of 18S:A543 was detected by primer extension on total RNA at low dNTP concentration (Maden, 2001). Prematurely reverse transcriptase arrest one nucleotide before the methylated residue is shown by an asterisk. The 18S rRNA/snoR43.1 duplex is shown, and the target A543 is indicated by a black circle. (D) Expression of tsnoR43 genes detected by RT–PCR. The RT–PCR on total RNA from Arabidopsis seedlings was performed with p1 and each of the reverse primers as indicated: +RT and –RT refer to the presence and absence, respectively, of reverse transcriptase in the RT–PCR assay. The gDNA is a PCR reaction performed with genomic DNA as template for a size control to compare with the RT–PCR product. M is a DNA 100 bp ladder.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.