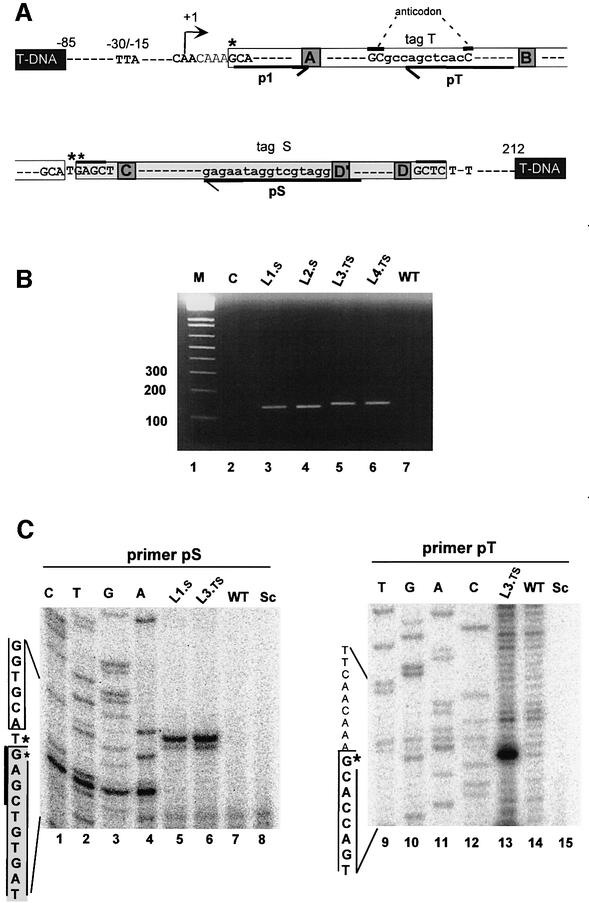
Fig. 4. Expression of tagged tRNAGly.t–snoR43.s in transgenic Arabidopsis lines. (A) Structure of the tagged tRNAGly.t–snoR43.s transgene. The TIS, nucleotide +1, is indicated by an arrow. The conserved elements controlling tRNA gene expression and snoRNA accumulation are indicated. White and grey boxes indicate the mature tRNA and snoRNA with their terminal sequences, respectively. The terminal inverted repeats of snoR43.1 are indicated by thick overlines. The tag t inserted in the GCC anticodon and the tag s replacing the antisense rRNA element adjacent to the D′ box are in lower-case letters. Black boxes indicate T-DNA flanking sequences. Four transgenic lines were produced: s-tagged L1.s and L2.s and ts-tagged L3.ts and L4.ts. Primers used for RT–PCR and primer extension analysis are indicated by p1, pt and ps. The asterisks indicate the positions of the primer extension signals detected in (C). (B) Detection of the dicistronic tagged precursors by RT–PCR. The assay was performed using primers p1/ps on total RNA extracted from transgenic lines L1.s, L2.s, L3.ts and L4.ts or wild-type (WT) non-transgenic plants as indicated. C is a control RT–PCR using total RNA from L1.s as substrate but omitting reverse transcriptase in the reaction. M indicates 100 bp DNA size markers. (C) Detection of tagged AtsnoR43.s and tRNAGly.ts by primer extension. Reverse transcription was performed with primers ps or pt and total RNA from transgenic lines L1.s and L3.ts and non-transgenic lines WT, as indicated. Sc is a control with yeast tRNA. CTAG is the sequence ladder of tRNAGlyt–snoR43.s gene. The tRNA and snoRNA sequences are indicated by white and grey boxes, respectively, on the left of the gels. The asterisks indicate the position of the extension signals.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.