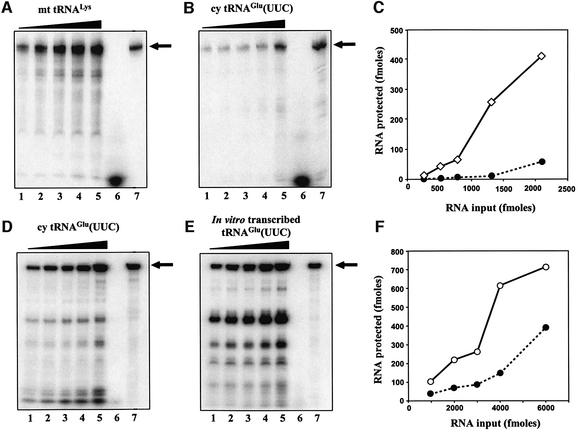
Fig. 6. (A and B) In vitro importation assays of affinity-purified mt tRNALys and cy tRNAGlu. Both pCp-labeled tRNAs were gel purified and resuspended at the same concentration and specific activity. Lanes 1–5: increasing concentrations (263, 526, 789, 1315 and 2105 fmol) of tRNA incubated with mitochondria and digested with MNase. Lane 6: 1000 fmol of tRNA digested with MNase. Lane 7: 10 fmol of the input RNA (IN). (D and E) In vitro importation assays of cy tRNAGlu and its transcript. Lanes 1–5: increasing concentrations (1000, 2000, 3000, 4000 and 6000 fmol) of RNA incubated with mitochondria and digested with MNase. Lane 6: 1000 fmol of tRNA digested with MNase. Lane 7: 19 fmol of the input RNA (IN). The RNAs were resolved by electrophoresis on 7 M urea/10% acrylamide gels for (A) and (B), or 7 M urea/8% acrylamide gels for (D) and (E). The migration of the full-length RNAs is indicated by an arrow. (C and F) The results showing nuclease protection of the pCp-labeled tRNAs incubated with isolated L.tarentolae mitochondria. Full-length RNAs protected from nuclease digestion were quantitated for native mt tRNALys (diamonds), native cy tRNAGlu (filled circles) and T7-transcribed tRNAGlu (open circles).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.