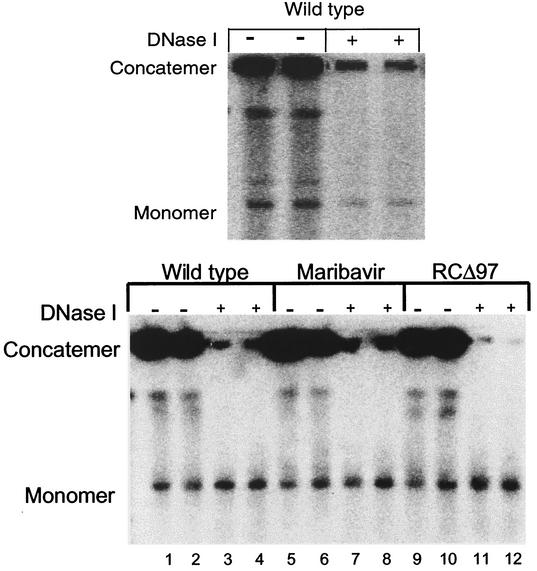
FIG. 4.
Analysis of viral DNA cleavage and packaging by using DNase I. (Top panel) Cells were infected at an MOI of 1 with wt HCMV in the absence of drug. At 72 h p.i., aliquots of infected cells were embedded in agarose and either lysed with SDS and proteinase K immediately (lanes −) or treated with DNase I before lysis (lanes +). (Bottom panel) Cells were infected at an MOI of 1 with wt HCMV in the absence of drug (lanes 1 to 4) or in the presence of 1 μM maribavir (lanes 5 to 8) or with RCΔ97 in the absence of drug (lanes 9 to 12). At 72 h p.i., aliquots of infected cells were embedded in agarose and either lysed with SDS and proteinase K immediately (lanes 1, 2, 5, 6, 9, and 10) or, following equilibration with 0.5 M EDTA (pH 9), treated with DNase I and then lysed (lanes 3, 4, 7, 8, 11, and 12). In both panels, the DNA was resolved by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. In the top panel, the gel was stained with ethidium bromide and photographed. Subsequent blotting and hybridization confirmed the locations of monomer and concatemer (data not shown). In the bottom panel, the DNA was transferred to a nylon membrane and hybridized for virus-specific sequences with a radiolabeled probe. The positions of DNA concatemers that remain in the well of the gel and monomer (genome-length) HCMV DNA are indicated.