Abstract
In an in vitro autologous system, studies were carried out on the transfer of either biosynthetically-labelled [14C]Salmonella enteritidis endotoxin or [125I]Maia squinado haemocyanin from macrophages to lymphocytes.
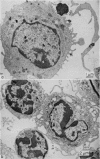
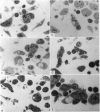
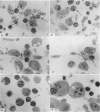
When cultured 1 hour in vitro, lymphocytes adhered to autologous macrophages, forming lymphocyte-macrophage islands (LMI).
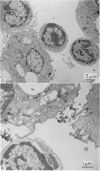
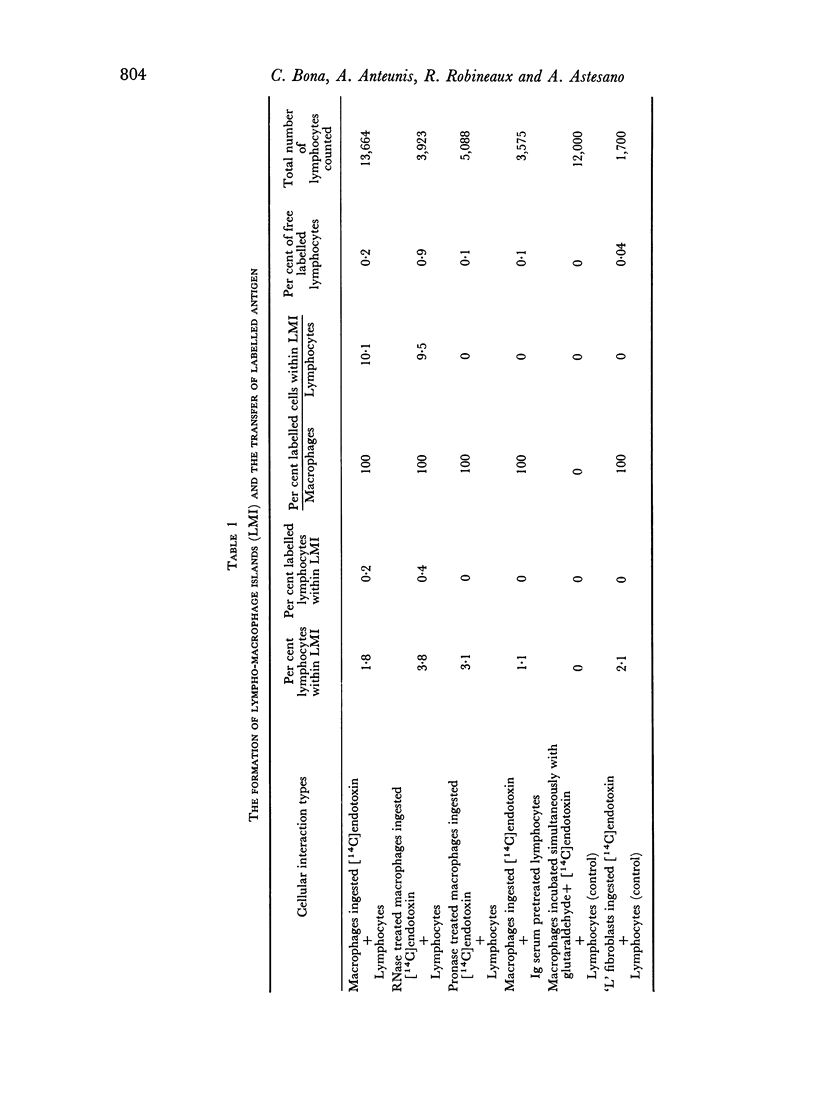
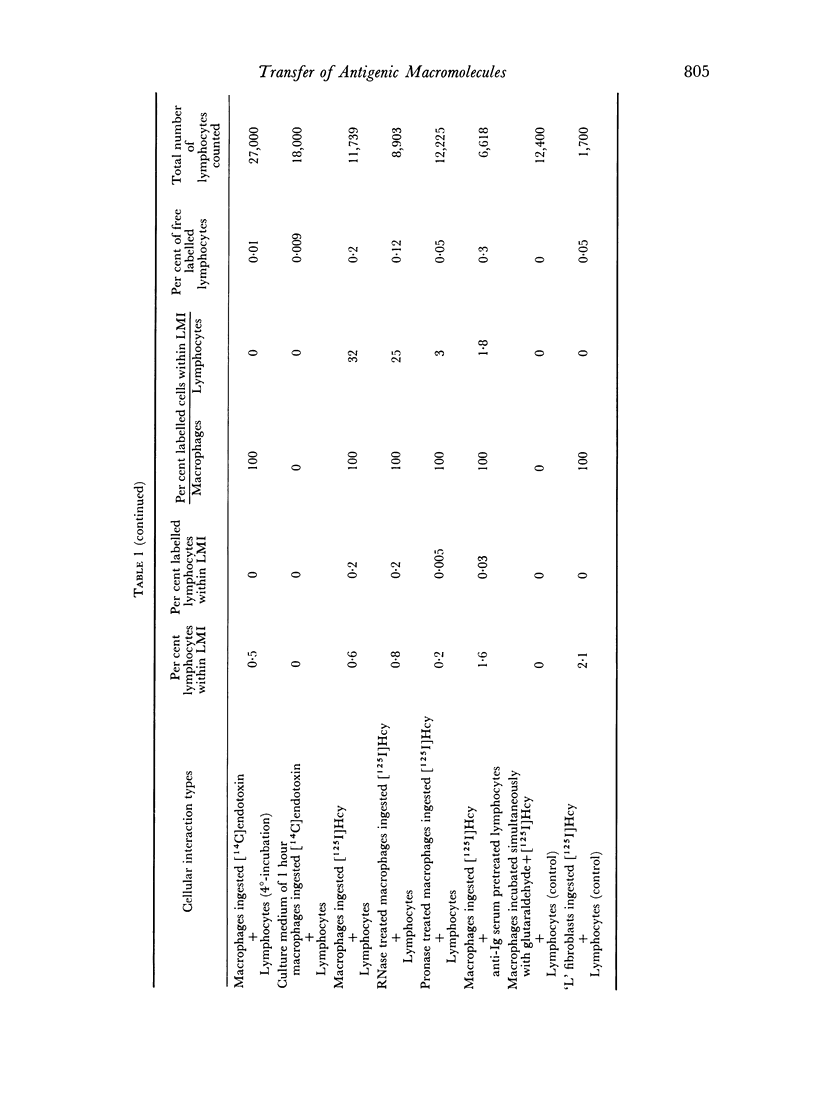
Quantitative data obtained from stained thick sections showed that 1.8 per cent of the lymphocytes had adhered to macrophages with ingested [14C]endotoxin while 0.6 per cent of the lymphocytes adhered to macrophages with ingested [125I]haemocyanin. The presence of antigen macromolecules was observed mainly within lymphocytes adhering to macrophages with ingested antigens, i.e. at the level of LMI. On the other hand, autoradiography carried out on the same thick sections, showed that 0.20 per cent of the lymphocyte population in LMI possess silver grains. High resolution autoradiographic pictures of thin sections, showed a peculiar localization of silver grains in LMI lymphocytes: about 80 per cent of the radioactivity was found within lymphocytic nuclei and the remainder either on the cellular membrane or free in the cytoplasm. The disappearance of radioactivity from the LMI-located macrophage membranes (where lymphocytes contain silver grains) as well as the regular inhibition of antigen transfer occurring after pronase treatment of the macrophage which contained ingested antigen, strongly suggest that antigen bound to macrophage membrane was transferred to lymphocytes. As pretreatment of lymphocytes with anti-Ig serum resulted in regular inhibition of antigen transfer, it appears that the Ig receptors of lymphocyte membranes play an important role in the transfer mechanism.
Combined technique, i.e. autoradiography and the peroxidase method for revealing Ig bound to lymphocyte membranes, showed that silver grains occurred only within lymphocytes displaying peroxidase-positive membrane.
Full text
PDF



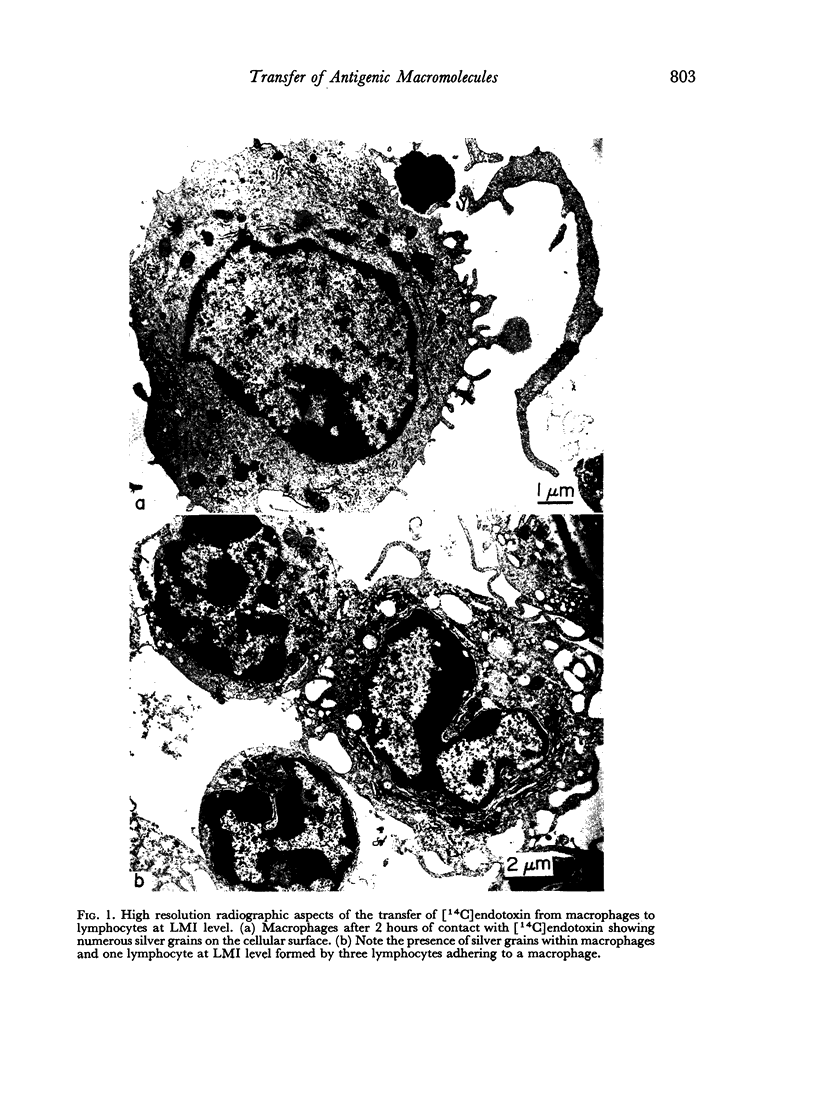
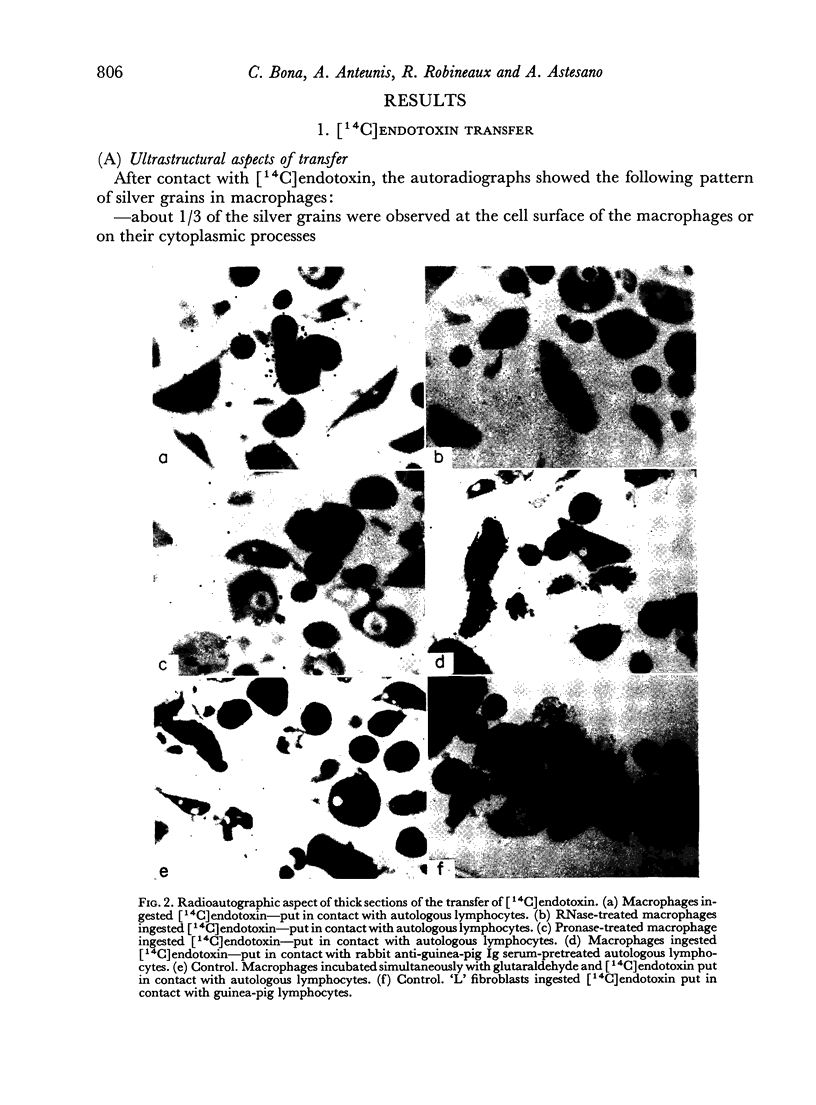


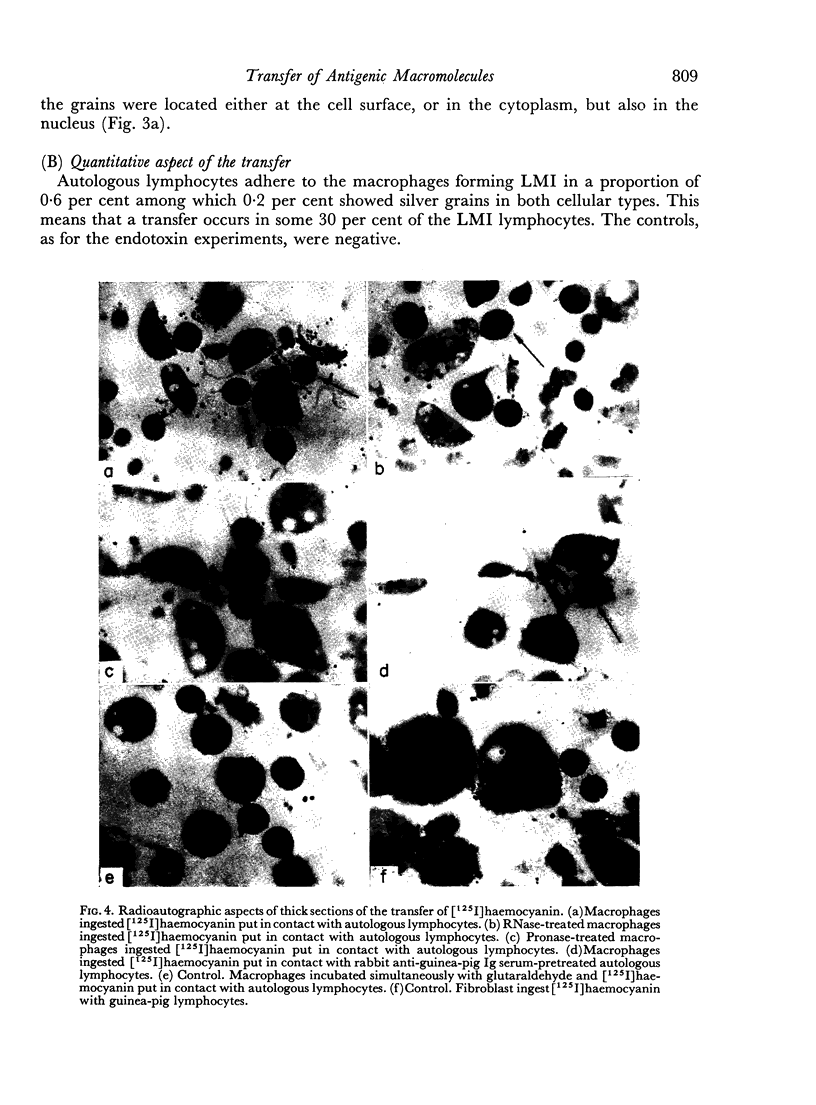
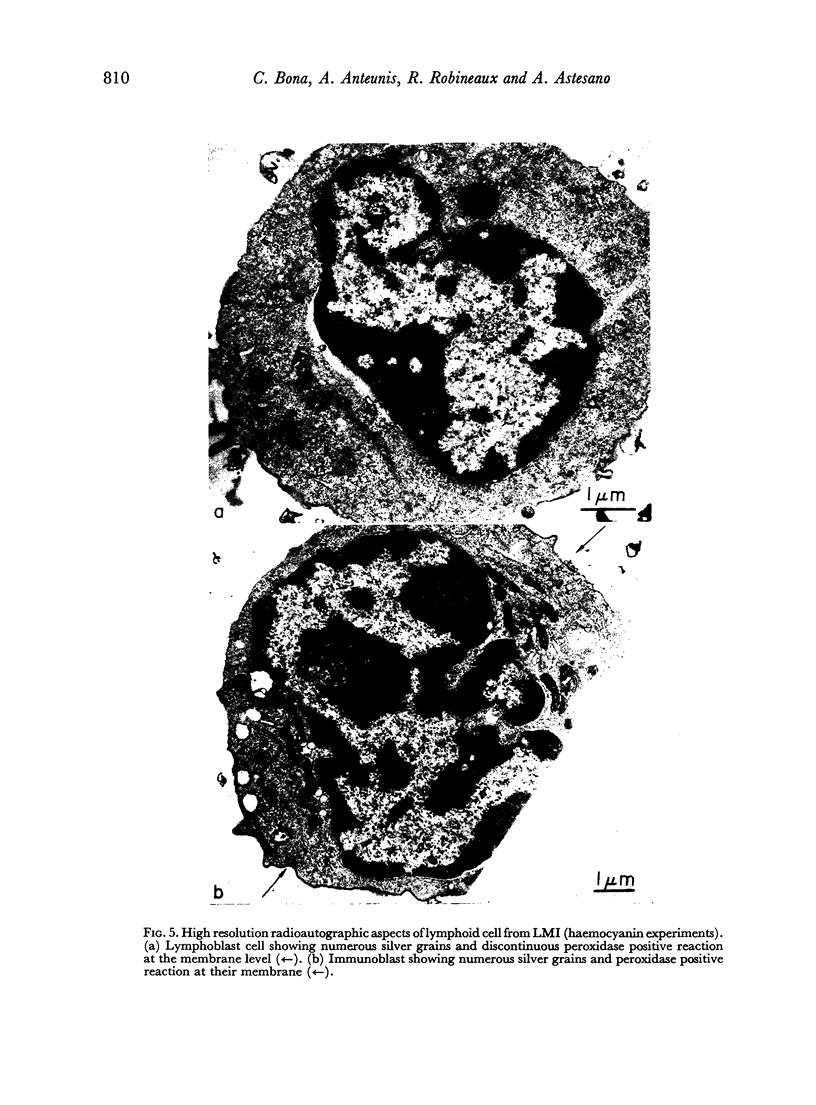






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARONSON M. BRIGE FORMATION AND CYTOPLASMIC FLOW BETWEEN PHAGOCYTIC CELLS. J Exp Med. 1963 Dec 1;118:1083–1088. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.6.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASKONAS B. A., RHODES J. M. IMMUNOGENICITY OF ANTIGEN-CONTAINING RIBONUCLEIC ACID PREPARATIONS FROM MACROPHAGES. Nature. 1965 Jan 30;205:470–474. doi: 10.1038/205470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler F. L., Fishman M., Dray S. Antibody formation initiated in vitro. 3. Antibody formation and allotypic specificity directed by ribonucleic acid from peritoneal exudate cells. J Immunol. 1966 Oct;97(4):554–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S. Détection d'anticorps et d'antigènes a l'air d'enzymes. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1968 Sep 28;50(5):1169–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. C., Pisciotta A. V., Abramoff P. Synthesis of normal and "immunogenic RNA" in peritoneal macrophage cells. J Immunol. 1967 Oct;99(4):751–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bona C., Anteunis A., Robineaux R., Astesano A. Etude radioautographique ultrastructurale du transfert in vitro d l'ARN immunogène produit par les macrophages qui ont capté l'endotoxine de Salmonella typhimurium S. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1969 Sep;269(12):1145–1147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Swett V. C. The interaction of human monocytes and lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Dec 1;128(6):1309–1325. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.6.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresser D. W., Mitchison N. A. The mechanism of immunological paralysis. Adv Immunol. 1968;8:129–181. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60466-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN M. Antibody formation in vitro. J Exp Med. 1961 Dec 1;114:837–856. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.6.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN M., HAMMERSTROM R. A., BOND V. P. In vitro transfer of macrophage RNA to lymph node cells. Nature. 1963 May 11;198:549–551. doi: 10.1038/198549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREI P. C., BENACERRAF B., THORBECKE G. J. PHAGOCYTOSIS OF THE ANTIGEN, A CRUCIAL STEP IN THE INDUCTION OF THE PRIMARY RESPONSE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jan;53:20–23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. P., Stavitsky A. B., Solomon J. M. Induction in vitro of antibodies to phage T2: antigens in the RNA extract employed. Science. 1965 Sep 3;149(3688):1106–1107. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3688.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallily R., Feldman M. The induction of antibody production in x-irradiated animals by macrophages that interacted with antigen. Isr J Med Sci. 1966 May-Jun;2(3):358–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb A. A., Glisin V. R., Doty P. Studies on macrophage RNA involved in antibody production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1849–1856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F. Biological effects of anti-immunoglobulins: evidence for immunoglobulin receptors on 'T' and 'B' lymphocytes. Transplant Rev. 1970;5:45–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1970.tb00356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanifin J. M., Cline M. J. Human monocytes and macrophages. Interaction with antigen and lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jul;46(1):97–105. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. S., Johnson A. G. Radioautographic and electron-microscopic evidence of rapid uptake of antigen by lymphocytes. Science. 1966 Jul 8;153(3732):176–178. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3732.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna M. G., Jr, Szakal A. K. Localization of 125I-labeled antigen in germinal centers of mouse spleen: histologic and ultrastructural autoradiographic studies of the secondary immune reaction. J Immunol. 1968 Nov;101(5):949–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haurowitz F. Struktur und Wirkungsweise der Antikörper. Naturwissenschaften. 1969 Apr;56(4):189–194. doi: 10.1007/BF01166813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh E. M., Harris J. E. Macrophage-lymphocyte interaction in the antigen-induced blastogenic response of human peripheral blood leukocytes. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1184–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M., Spurná V. Interaction of mouse leukemic cells with L cells in tissue culture. I. Passage of leukemic cell DNA into the nuclei of L cells. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Apr;50(1):208–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90408-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. H., Frank M. M. The localization of non-microbial antigens in the draining lymph nodes of tolerant, normal and primed rabbits. Immunology. 1967 Jul;13(1):87–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. H. The fate of antigen and its relationship to the immune response. The complexity of antigens. Antibiot Chemother. 1969;15:7–23. doi: 10.1159/000386767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno Y., Loewenstein W. R. Cell-to-cell passage of large molecules. Nature. 1966 Nov 5;212(5062):629–630. doi: 10.1038/212629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduc E. H., Scott G. B., Avrameas S. Ultrastructural localization of intracellular immune globulins in plasma cells and lymphoblasts by enzyme-labeled antibodies. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 Apr;17(4):211–224. doi: 10.1177/17.4.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCFARLAND W., HEILMAN D. H. LYMPHOCYTE FOOT APPENDAGE: ITS ROLE IN LYMPHOCYTE FUNCTION AND IN IMMUNOLOGICAL REACTIONS. Nature. 1965 Feb 27;205:887–888. doi: 10.1038/205887a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE R. D., MUMAW V. R., SCHOENBERG M. D. The transport and distribution of colloidal iron and its relation to the ultrastructure of the cell. J Ultrastruct Res. 1961 Jun;5:244–256. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(61)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O., Askonas B. A., Humphrey J. H., Schechter I., Sela M. The localization of antigen in relation to specific antibody-producing cells. I. Use of a synthetic polypeptide [(T,G)-A--L] labelled with iodine-125. Immunology. 1966 Oct;11(4):337–351. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J., Abbot A. Antigens in immunity. XVI. A light and electron microscope study of antigen localization in the rat spleen. Immunology. 1971 Aug;21(2):207–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J., Abbot A. Ultrastructure of the antigen-retaining reticulum of lymph node follicles as shown by high-resolution autoradiography. Nature. 1965 Oct 30;208(5009):500–502. doi: 10.1038/208500b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison N. A. The immunogenic capacity of antigen taken up by peritoneal exudate cells. Immunology. 1969 Jan;16(1):1–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi S., Kurashige S., Kawakami M., Nojima T. Transfer agent of immunity. I. Immune ribonucleic acid which induces antibody formation to Salmonella flagella. Jpn J Microbiol. 1968 Sep;12(3):261–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E. A requirement for two cell types for antibody formation in vitro. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1573–1575. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Coppleson L. W. A THREE-CELL INTERACTION REQUIRED FOR THE INDUCTION OF THE PRIMARY IMMUNE RESPONSE in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):542–547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Ferris B., Hirsch J. G. Macrophage plasma membranes. I. Isolation and studies on protein components. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):785–806. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Abbot A., Mitchell J. Antigens in immunity. XIV. Electron microscopic radioautographic studies of antigen capture in the lymph node medulla. J Exp Med. 1968 Feb 1;127(2):263–276. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.2.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Abbot A., Mitchell J., Lummus Z. Antigens in immunity. XV. Ultrastructural features of antigen capture in primary and secondary lymphoid follicles. J Exp Med. 1968 Feb 1;127(2):277–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Self-recognition. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun 30;124(1):37–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb18940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paque R. E., Dray S. Interspecies "transfer" of delayed hypersensitivity in vitro with RNA extracts. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1334–1338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribnow J. F., Silverman M. S. Studies on the radiosensitive phase of the primary antibody response in rabbits. I. The role of the macrophage. J Immunol. 1967 Feb;98(2):225–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIBI E., HASKINS W. T., LANDY M., MILNER K. C. Preparation and host-reactive properties of endotoxin with low content of nitrogen and lipid. J Exp Med. 1961 Nov 1;114:647–663. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.5.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS A. N., HAUROWITZ F. Intracellular localization and quantitation of tritiated antigens in reticuloendothelial tissues of mice during secondary and hyperimmune responses. J Exp Med. 1962 Oct 1;116:407–422. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.4.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINEAUX R., PINET J., KOURILSKY R. [Morphodynamic study of reticular lympho-plasmocytic islets in culture under a dialysis membrane]. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1962;156:1025–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robineaux R., Anteunis A., Bona C. Ultrastructure des macrophages de cobaye. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Mar;120(3):329–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOENBERG M. D., MUMAW V. R., MOORE R. D., WEISBERGER A. S. CYTOPLASMIC INTERACTION BETWEEN MACROPHAGES AND LYMPHOCYTIC CELLS IN ANTIBODY SYNTHESIS. Science. 1964 Feb 28;143(3609):964–965. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3609.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel I. Natural and antibody-induced adherence of guinea pig phagocytic cells to autologous and heterologous thymocytes. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):879–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilard L. THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ANTIBODY FORMATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):293–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TATA J. R. The partial purification and properties of thyroxine dehalogenase. Biochem J. 1960 Nov;77:214–226. doi: 10.1042/bj0770214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIERY J. P. Etude sur le plasmocyte en contraste de phase et en microscopie électronique. III. Plasmocytes à corps de Russell et à cristaux. Rev Hematol. 1958 Jan-Mar;13(1):61–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P. Ultrastructure et fonctions des cellules impliquées dans la réaction immunitaire. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1968 Sep 28;50(5):1077–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Askonas B. A. The immune response of mice to antigen in macrophages. Immunology. 1968 Aug;15(2):287–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Cerottini J. C., Bedford M. Persistence of antigen on the surface of macrophages. Nature. 1969 Jun 21;222(5199):1193–1195. doi: 10.1038/2221193a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Cerottini J. C. The immunogenicity of antigen bound to the plasma membrane of macrophages. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):711–725. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. The immune response of mice to keyhole limpet hemocyanin bound to macrophages. J Immunol. 1969 Apr;102(4):893–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLENSIEK H. J., COONS A. H. STUDIES ON ANTIBODY PRODUCTION. IX. THE CELLULAR LOCALIZATION OF ANTIGEN MOLECULES (FERRITIN) IN THE SECONDARY RESPONSE. J Exp Med. 1964 Apr 1;119:685–696. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.4.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]