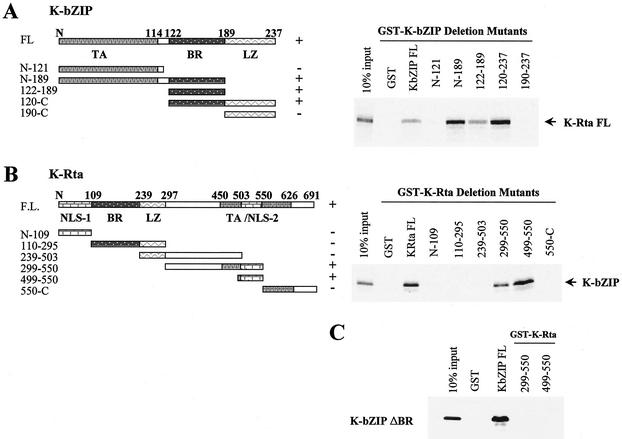
FIG. 3.
In vitro interactions and interacting domains of both K-bZIP and K-Rta. (A) The domains of K-bZIP and the GST-K-bZIP mutants are indicated in the left panel. FL, full length; TA, transactivation domain; BR, basic region; LZ, leucine zipper domain. The results of GST pull-down assays for in vitro-translated, 35S-labeled full-length K-Rta and deletion mutants of K-bZIP are shown in the right panel. Pull-down-positive clones are indicated by plus signs. (B) The domains of K-Rta and the GST-K-Rta mutants are indicated in the left panel. NLS, putative nuclear localization signal. The results of GST pull-down assays for in vitro-translated, 35S-labeled full-length K-bZIP and deletion mutants of K-Rta are shown in the right panel. (C) Results of GST pull-down assays for in vitro-translated, 35S-labeled K-bZIPΔBR and K-Rta mutants. Full-length GST-K-bZIP was used as a positive control.