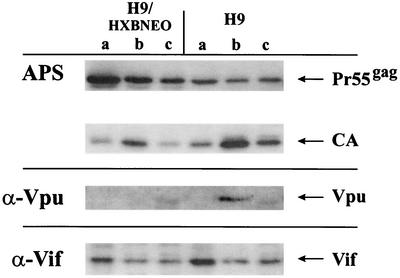
FIG. 4.
Intracellular distribution of Vif in chronically and acutely infected H9 cells. Chronically (H9/HXB2NEO) or acutely (H9) infected cells were fractionated into soluble (a), detergent-soluble (b), and detergent-resistant (c) fractions as described in Materials and Methods. Cell lysates were separated by SDS-13% PAGE, transferred to PVDF membranes, and subjected to immunoblotting using an HIV-positive patient serum (APS) for detection of Pr55gag and CA, a Vpu-specific polyclonal antibody (U2-3) for detection of Vpu (α-Vpu), or monoclonal antibody MAb #319 for detection of Vif (α-Vif). Proteins were visualized by ECL using appropriate horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies. A minor nonspecific protein cross-reacting with the Vpu antiserum is visible in fractions c of both cell types.