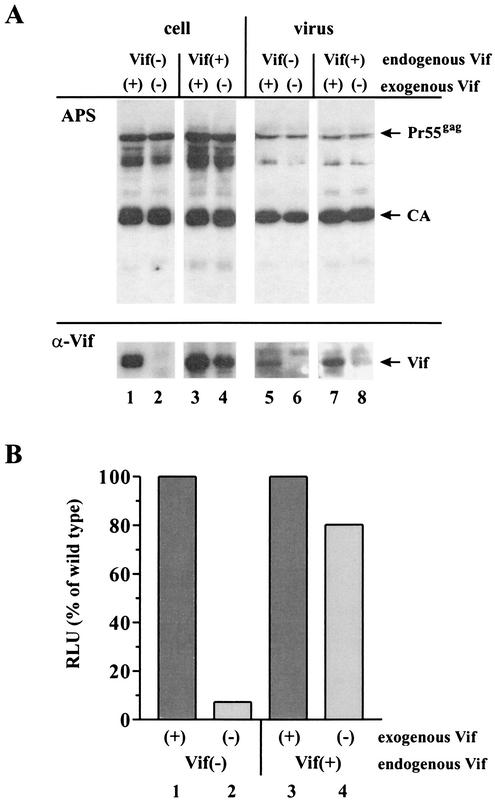
FIG. 6.
Rescue of viral infectivity by endogenous Vif. (A) H9/HXB2NEO [Vif(+)] and H9/HXB2VifΔNEO [Vif(−)] cells (5 × 106 each) were electroporated with a combination of pHCMV-G (5 μg) and 15 μg of either pNL4-3 [(+)] or pNL4-3 Vif(−) [(−)] plasmid DNAs. Cells and virus-containing supernatants were harvested 24 h after electroporation. Virus from 50% of the supernatant was concentrated by ultracentrifugation through 20% sucrose and suspended in 200 μl of sample buffer. Cells were washed once with PBS, and whole-cell lysates were prepared by suspending cells in 150 μl of PBS plus 150 μl of sample buffer. Viral and cell lysates were boiled (95°C, 15 min), and 30 μl of cell lysates and 90 μl of viral lysates were subjected to SDS-13% PAGE. Proteins were transferred to PVDF membranes and subjected to immunoblotting using MAb #319 (α-Vif). The same blot was subsequently reacted with an HIV-positive patient serum (APS). Proteins are identified on the right. (B) Unconcentrated virus-containing supernatants (500 μl each) from panel A were used to infect LuSIV indicator cells. Input virus was quantified both by reverse transcriptase assay and p24 ELISA, and relative infectivity of the viruses was determined by quantifying the virus-induced luciferase activity as described in Materials and Methods. RLU, relative light units.