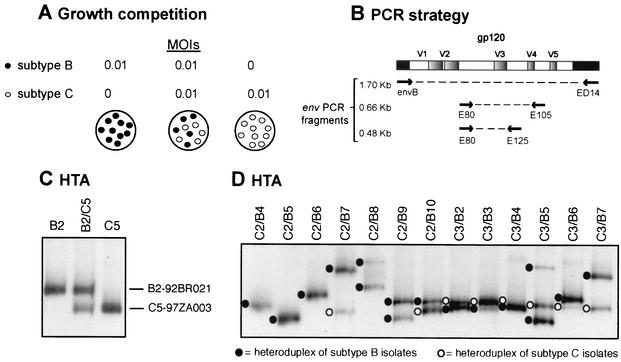
FIG. 2.
Strategy for HIV-1 competition experiments and heteroduplex tracking method for dual virus detection and quantification. (A) Virus was added alone or in pairs to phytohemagglutinin- and interleukin-2-treated PBMC at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.01. Cells were washed after 8 h to remove virus. Cells and virus supernatant was harvested at day 10 and lysed. (B) Extracted DNA or RNA from dual infections was PCR or RT-PCR amplified with conserved HIV-1 env primers. PCR-amplified env products were denatured, annealed to a radiolabeled env probe, and then run on an 8% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel (C and D). Heteroduplexes generated from monoinfections (C) were then used to identify those isolates found in the heteroduplex tracking analysis (HTA) of each dual infection (D). Phosphor-imaging analysis of each heteroduplex was used to quantify the production of each virus in a dual infection. Multiple heteroduplexes can track to a single HIV-1 isolate because these isolates represent the propagated quasispecies and not a single clone.