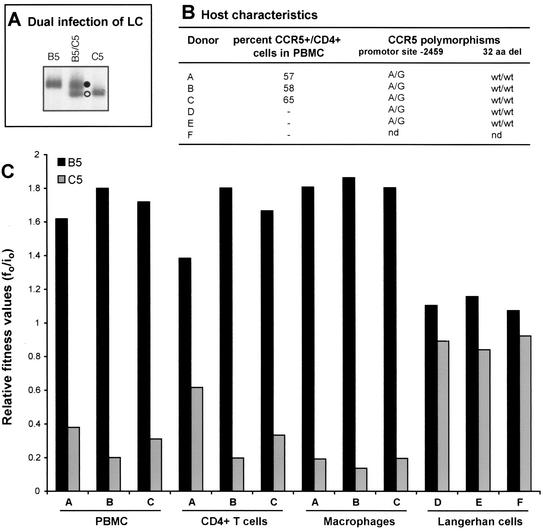
FIG. 5.
Comparing the relative fitness values of B5 and C5 HIV-1 isolates derived from competitions in CD4+ T cells, macrophages, and skin-derived Langerhans cells from different donors. (A) An example of B5 and C5 monoinfections and dual infection of skin-derived Langerhans cells (LC) from donor D. Skin explants were obtained from suction blister roofs isolated from the thighs of healthy donors (35) and exposed to a multiplicity of infection of 0.01 of the virus (250 IU added to approximately 25,000 Langerhans cells embedded within each skin explant). Langerhans cells were then allowed to emigrate from explants and were harvested on day 3 or 4 postinfection. DNA extracted from lysed cells was subjected to HIV-specific PCR amplifications and heteroduplex tracking analysis. Purification and subsequent HIV infections of macrophages and CD4+ T cells were done as described in Materials and Methods. Similar heteroduplex tracking analyses were performed on these samples. (B) Genetic characteristics and coreceptor expression on host PBMC cells. T cells and macrophages were purified from PBMC from three donors. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis was performed on the PBMC populations prior to cell isolation to measure CCR5 and CD4 expression. PBMC labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled anti-CD4 antibody and phycoerythrin-labeled anti-CCR5 antibodies were analyzed with the FACScan flow cytometer and Lysis II software (44). Percentages represent the fraction of CCR5-positive cells in the CD4-positive-gated lymphocyte population. Genetic polymorphisms at position −2459 in CCR5 promoter and the presence or absence of a 32-codon deletion (32 aa del) in the CCR5 open reading frame were also determined. wt, wild type; nd, not determined. (C) Relative fitness of the B5 and C5 HIV-1 isolates derived from dual infection of PBMC, CD4+ T cells, macrophages, and skin-derived Langerhans cells from different donors. Relative fitness value was measured as the proportion of each virus produced from the dual infection (f0) divided by the initial fraction of that virus added to the culture (i0) (62).