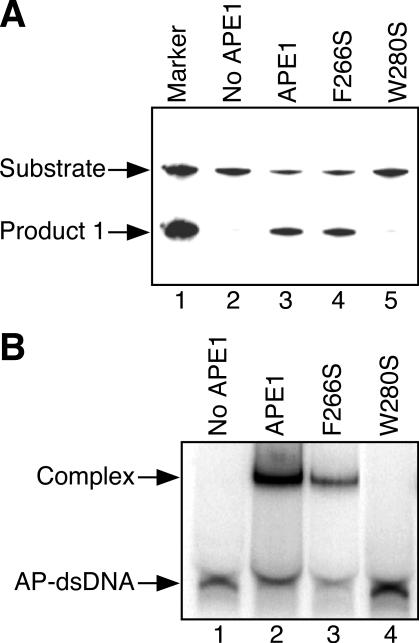
Figure 3.
Influence of substitutions of the aromatic amino acid residues around the active site of human APE1. (A) Detection of products of cleavage by wild-type APE1 and its mutant proteins. Substrate DNA (AP-dsDNA: 4.4 pmol), in which the oligonucleotide containing an AP site was 5′ 32P-labeled, was incubated with the wild-type APE1 or its mutant (0.04 pmol). The DNA products were analyzed by 20% denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. (B) Binding of APE1 and its mutant proteins to the dsDNA containing an AP site (AP-dsDNA). AP-dsDNA (0.45 pmol) was incubated with the wild-type APE1 or its mutants (4.5 pmol). Protein–DNA complex was analyzed by 15% native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.