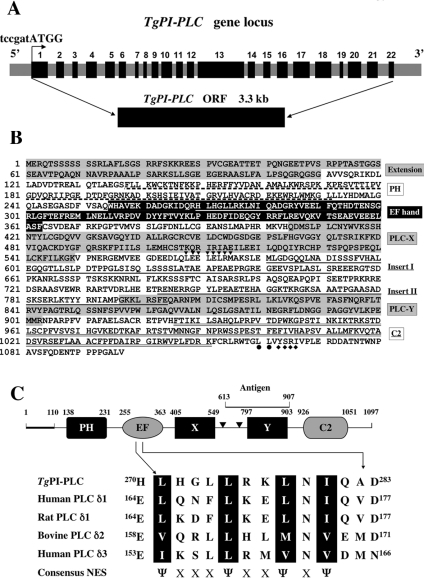
Figure 1. Organization and predicted protein sequence of TgPI-PLC.
(A) Schematic map of the TgPI-PLC gene locus. The relative position of exons in the genomic DNA is indicated by black boxes with numbers. The grey boxes show the 5′ end flanking region, the introns and the 3′ end flanking region. A Kozak translation initiation site (tccgatATGG, where the lower-case letters indicate untranslated sequence) is indicated above with a bent arrow. The isolated TgPI-PLC cDNA clone (5.5 kb) contains a 3.3 kb ORF. (B) Deduced amino acid sequence of the TgPI-PLC cDNA clone. The unique N-terminal extension and the catalytic X and Y domains are highlighted in grey. The additional two inserts between the X and Y domains are underlined. The consensus NES of TgPI-PLC (H270LHGLLRKLNIQAD283) within the EF hand is underlined in white. An additional putative leucine-rich NES site (L568EELELRM575) predicted using NetNES 1.1 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetNES/) is indicated by downward-pointing triangles downstream of the X domain. The dileucine (L1060L1061) and a mammalian sorting YXXΦ motif (Y1063SRI1066) is indicated with closed circles and diamonds respectively under the sequence at the C-terminal tail. (C) The numbers show the starting and finishing amino acid for each domain. The bold line indicates the N-terminal extension and two triangles represent the inserts in the X-Y domain linker. The peptide used to generate polyclonal antibody against TgPI-PLC (Antigen) is indicated above the Y domain. The protein size is not to scale. The consensus NES of the EF hand domain is compared with those of other δ-type PLCs. The important hydrophobic residues are in black boxes. Ψ represents a hydrophobic residue (isoleucine, valine or methionine); X represents any amino acid.