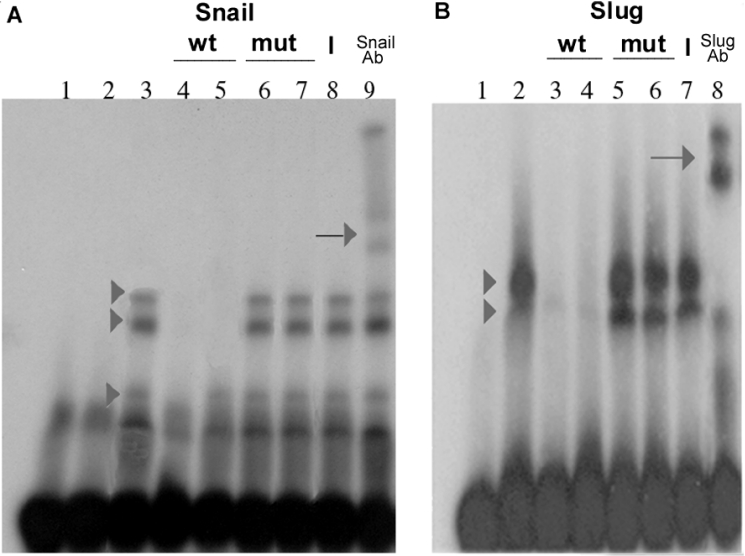
Figure 5. Direct binding of Snail and Slug to the E-boxes of the Claudin-1 promoter.
EMSA for the interaction of Snail and Slug with the E-box sequence. (A) Snail binding. Affinity-purified GST (lane 2) or GST–Snail (lanes 3–9) (10 ng) was incubated with double-stranded 32P-labelled oligonucleotides (2.5 ng) (+165 to +201) corresponding to the sequence containing two E-boxes of the Claudin-1 promoter; in lane 1, no protein was added. GST–Snail (arrowheads in lane 3), but not GST (lane 2), formed DNA complexes. Competitions were performed with a 200-fold excess of E1 (+153 to +192) and E2 (+176 to +215) wild-type probes (unlabelled oligonucleotides) (lanes 4 and 5), or mutant E1 and E2 boxes (lanes 6 and 7). Complex formation was affected by unlabelled wild-type E1 and E2 boxes, but not by unlabelled mutated boxes. Supershift experiments were performed by adding 200 ng of anti-Snail (lane 9) or non-specific (lane 8) antibody. Arrows in lane 9 indicate the supershifted retarded complexes. (B) Slug binding. Affinity-purified GST–Slug (lanes 2–8) (10 ng) was incubated with double-stranded 32P-labelled oligonucleotides (2.5 ng), containing E1 and E2 boxes (+165 to +201); in lane 1, no protein was added. GST–Slug formed two DNA complexes (arrowheads in lane 2). Competitions were performed with a 200-fold excess of wild-type E1 and E2 (lanes 3 and 4), or mutant E1 and E2 boxes (lanes 5 and 6). Results were very similar to those shown in (A). Supershift experiments were analysed by adding 200 ng of anti-Slug (lane 8) or non-specific (lane 7) antibody. Representative results from six independent experiments are shown. wt, wild-type; mut, mutant; Ab, antibody.