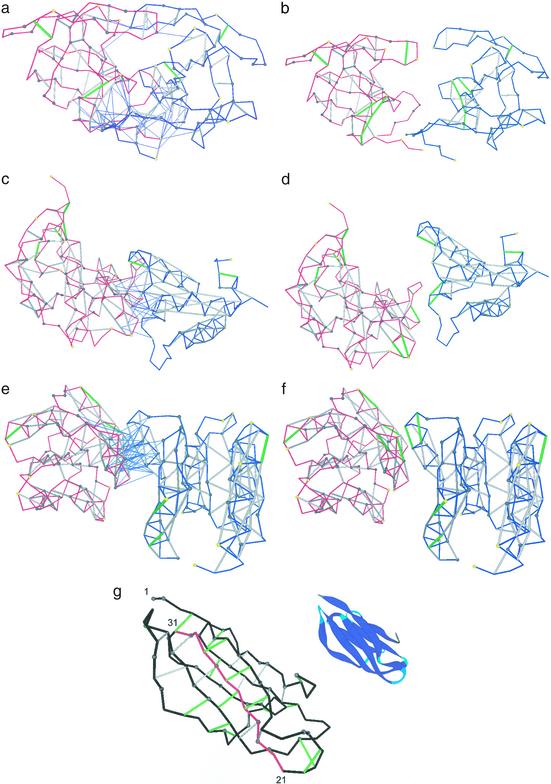
Figure 3.
Three selected complexes and separated binding partners for the HIV-1 protease dimer (PDB ID code 1a30, a and b), colicin + ligand (PDB ID code 1emv, c and d), and CheY complex (PDB ID code 1fqw, e and f). The binding partners are represented by blue and red virtual-bond backbone chains; the hydrophobic residues containing >1 carbonaceous group are denoted as α-carbon spheres: gray if the residue is >60% buried and yellow otherwise. The backbone hydrogen bonds are indicated as lines joining α-carbons: gray if the bond is sufficiently dehydrated and green if it is a UDHB. A thin blue line joining an α-carbon with a hydrogen-bond center indicates that a residue in one molecule is engaged in one or several intermolecular three-body correlations contributing to the dehydration of an intramolecular hydrogen bond of the binding partner. (g) Sufficiently dehydrated hydrogen bonds and UDHBs for monomeric β2-microglobulin. The segment with the highest concentration of structural defects is highlighted in red and is part of the so-called βB–βC (residues 21–33) amyloidogenic fragment generated by treatment of β2-microglobulin with Acromobacter protease (23). The ribbon picture is an aid to the eye.