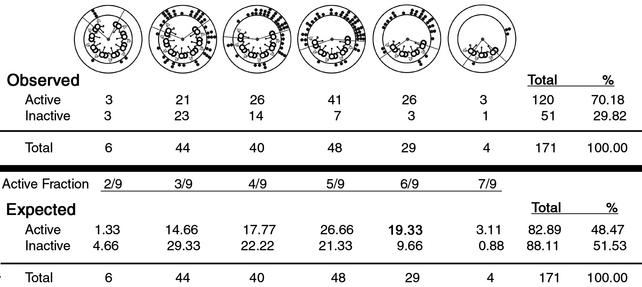
Figure 2.
Quantitative analysis of central apparatus orientation. The example shown is wild-type axonemes. We calculated the expected number of events for both the active and inactive areas for each pattern of microtubule sliding, if the orientation of the central apparatus was random. Expected events = (fraction of the axoneme in the active/inactive area) × (total events for sliding pattern). The expected events in the active area were totaled for all sliding patterns (Total), expressed as a percentage of the total number of transverse sections (%), and compared with the percentage of observed events.