Abstract
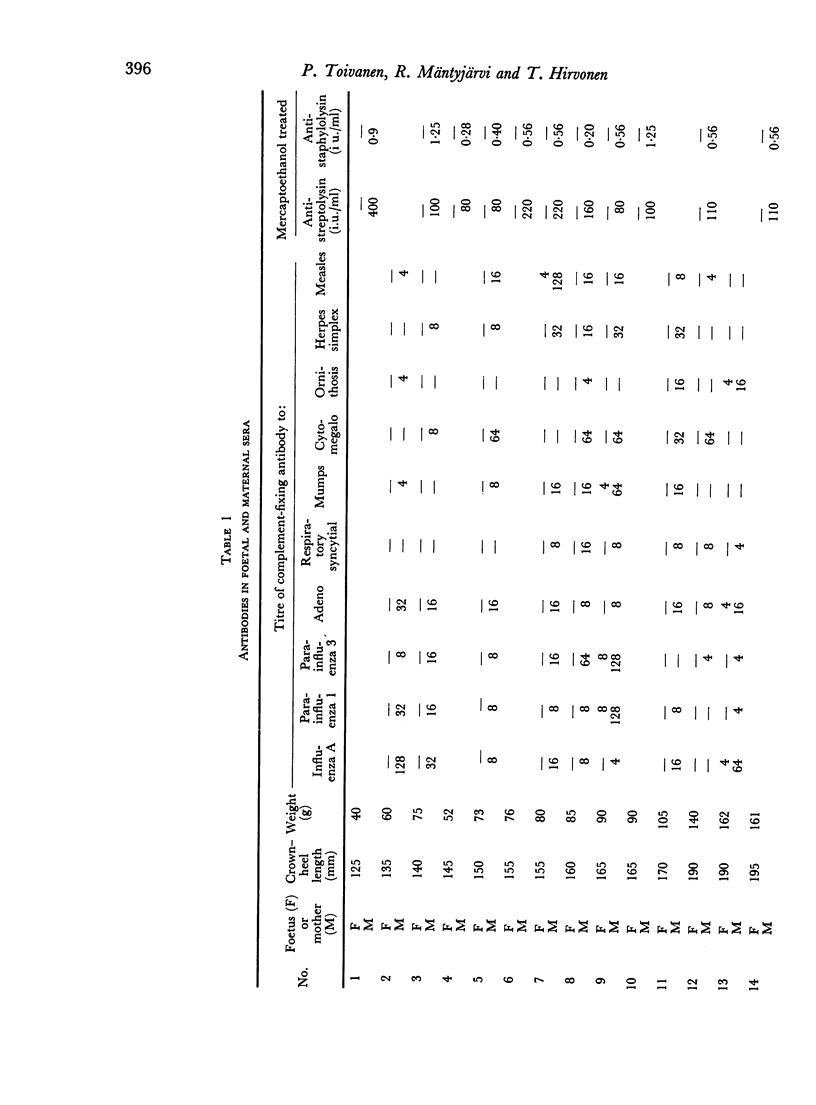
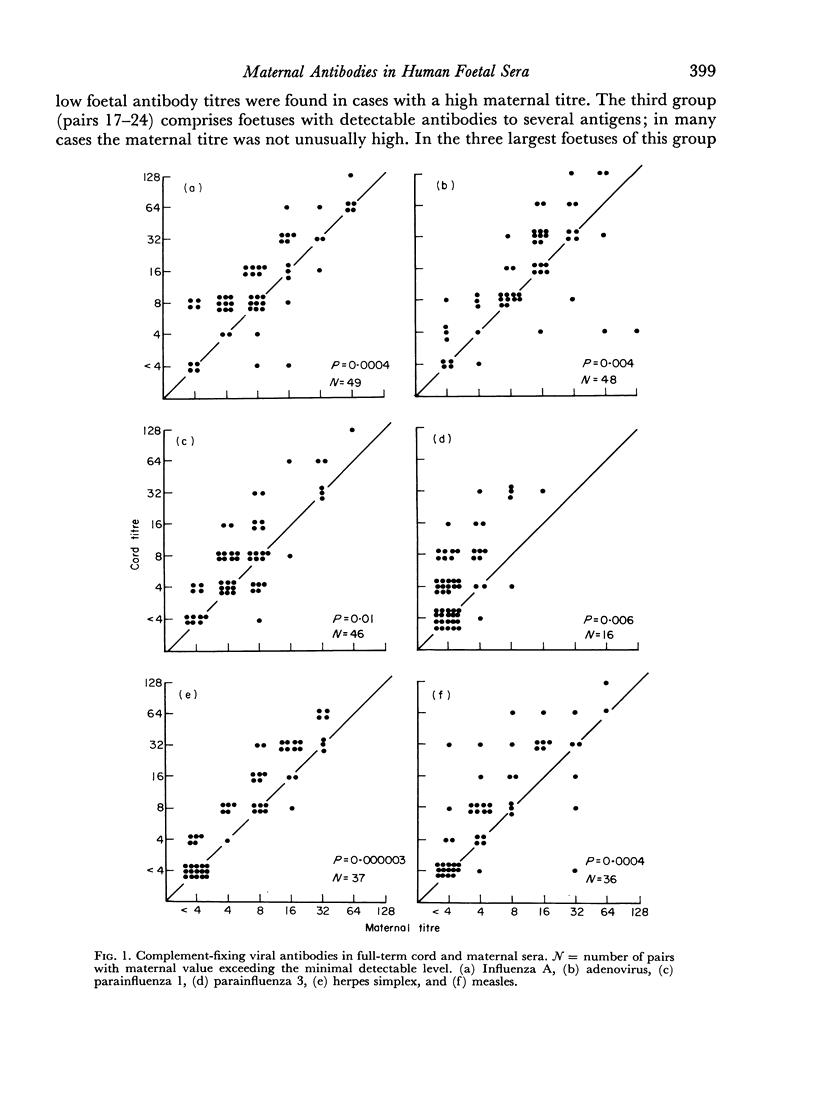
Complement-fixing antibodies to ten viral antigens and/or mercaptoethanol treated anti-streptolysin-O and anti-staphylolysin-α were determined in thirty human sera from foetuses at different stages of gestation, in fifty-seven full-term cord sera, and in the corresponding maternal sera. In the smallest foetuses (crown—heel length of 125–150 mm), no antibody was found. In those of length 155–215 mm, antibody was detectable if the corresponding maternal value was high. In foetuses of 230–380 mm, antibody was detected occasionally even when the maternal value was low. Sera of foetuses of 390 mm or more contained the same antibodies as the maternal sample, and foetal titres sometimes exceeded those of the mother. Titres in the full-term cord sera were significantly higher than the maternal titres for seven of the twelve antibodies studied.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buffe D., Burtin P. Formation des immunoglobulines chez le foetus et le jeune enfant. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1967 Apr;112(4):468–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S., PORTER R. B. STRUCTURE AND BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS. Adv Immunol. 1964;27:287–349. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60710-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON L. A., HOLM S. E. Precipitating antibodies in human sera from different age groups and in colostrum as determined by streptococcal antigens with diffusion-in-gel methods. Acta Paediatr. 1961 Jan;50:7–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1961.tb08016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. F., Farr R. S. Elevation of cord over maternal IgG immunoglobulin: evidence for an active placental IgG transport. Nature. 1966 Jun 4;210(5040):1070–1071. doi: 10.1038/2101070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN J. J., DANCIS J., ROSENBERG B. V. Studies of the immunology of the newborn infant. III. Permeability of the placenta to maternal antibody during fetal life. Pediatrics. 1952 Oct;10(4):450–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike R. M. Antibody heterogeneity and serological reactions. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Jun;31(2):157–174. doi: 10.1128/br.31.2.157-174.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAHLQUIST B., LAGERCRANTZ R., NORDBRING F. Maternal and foetal titres of antistreptolysin and antistaphylolysin at different stages of gestation. Lancet. 1950 Dec 23;2(6643):851–853. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(50)91782-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIENER A. S. The half-life of passively acquired antibody globulin molecules in infants. J Exp Med. 1951 Sep;94(3):213–221. doi: 10.1084/jem.94.3.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedermann G., Denk H., Kunz C. Komplementbindende Antikörper in Früh- und Spätstadien der Frühsommer-Meningoencephalitis (FSME) Z Immunitatsforsch Allerg Klin Immunol. 1967 Nov;134(2):160–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


