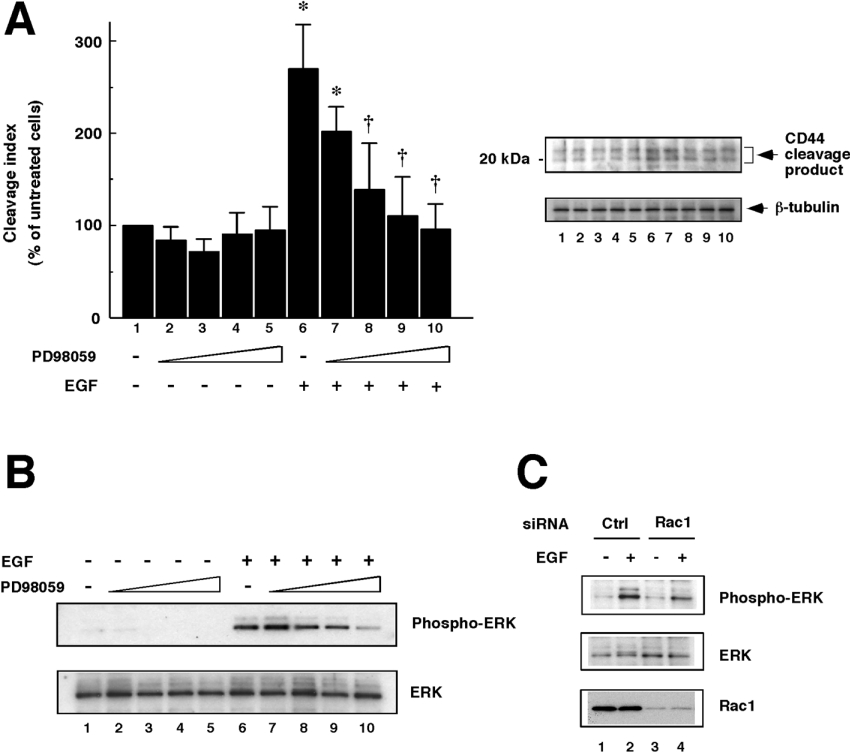
Figure 5. Involvement of ERK/MAPKs in EGF-induced CD44 cleavage.
(A) Effect of the MEK inhibitor PD98059 on EGF-induced CD44 cleavage. U251MG cells were pre-treated with 0 (lanes 1 and 6), 0.5 (lanes 2 and 7), 5 (lanes 3 and 8), 50 (lanes 4 and 9) or 100 (lanes 5 and 10) μM PD98059 for 30 min. The cells were treated with (lanes 6–10) or without (lanes 1–5) 10 ng/ml EGF for 1 h, and then lysed. CD44 cleavage was detected by Western blot analysis (upper panel). β-Tubulin was detected as an internal control (lower panel). The histogram shows the results of quantitative analysis of the CD44 cleavage product bands as means±S.D. for three independent experiments. *, P<0.01 compared with bar 1; †, P<0.01 compared with bar 6 (ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test). (B) Detection of activation of ERK/MAPKs. The cell lysates prepared as described above were subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-phosphorylated ERK pAb (upper panel) or anti-ERK pAb (lower panel). (C) Dependence of EGF-induced ERK/MAPK activation on Rac1. U251MG cells transfected with siRNA for Rac1 (lanes 3 and 4) or control scrambled siRNA (Ctrl; lanes 1 and 2) were incubated with (lanes 2 and 4) or without (lanes 1 and 3) 10 ng/ml EGF for 1 h. Thereafter, the cells were lysed and subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-phosphorylated ERK pAb (top panel) or anti-ERK pAb (middle panel). Bottom panel, detection of Rac1.