Fig. 1.
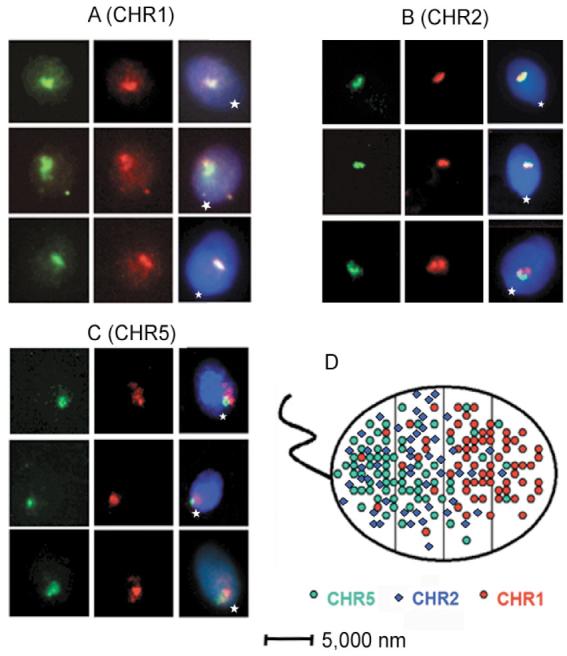
Compact CTs in human sperm nuclei. (A-C) Localization of chromosome arms using FISH with arm-specific microdissected DNA probes. Left panels, DIG-labeled q-arm probes detected with anti-DIG-FITC; middle panels, BIO-labeled p-arm probes detected with avidin-TR; right panels, images of the same cells registered using triple-band-pass filter, total DNA counterstained with DAPI. Position of the tail attachment (basal part of nuclei) is indicated by a star. (D) Non-random intranuclear localization of the compact CT of sperm chromosomes. Cumulative scheme, showing positions of CTs registered by FISH. Sperm cell nuclei is approximated by an ellipse and is divided into four zones, starting from the basal side that is determined by tail attachment site.
