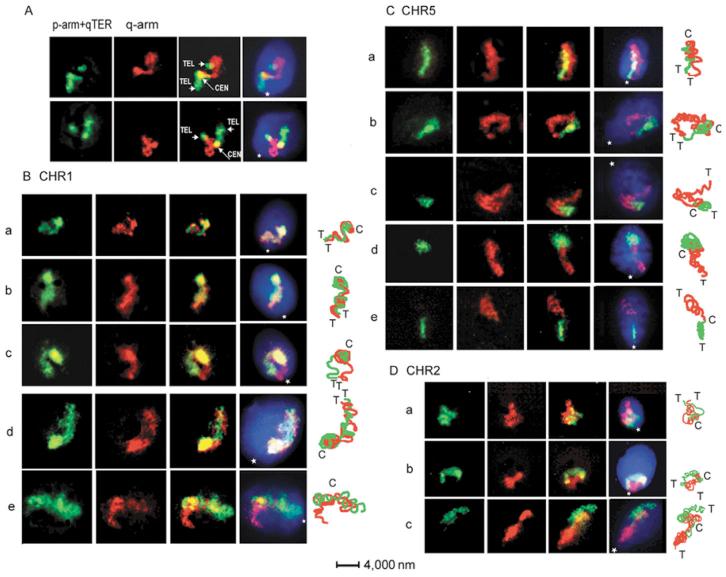
Fig. 2.
Internal organization of CTs. (A) Identification of the TEL and CEN domains in CHR5 using simultaneous hybridization with arm-specific and subTEL-specific probes. Both rows of panels from left to right: DIG-labeled p-arm painting and q-arm subTEL probes (qTER) were detected with anti-DIG-FITC; BIO-labeled q-arm probe was detected with avidin-TR; merged image and image registered with triple-band-pass filter, total DNA counterstained with DAPI. (B-D) Localization of chromosome-arm domains with two-color FISH (p-arms, green; q-arms, red). Representative sperm cells are shown in the three rows of panels (from left to right): images taken with a selective green-filter; images taken with a selective red-filter; merged red and green images; images acquired using triple-band-pass filter. To the right of images: matching schemes of the chromosome-arm paths indicating the localization of TEL (T) and CEN (C). Position of the tail attachment (basal part of nuclei) is indicated by a star.