Figure 8.
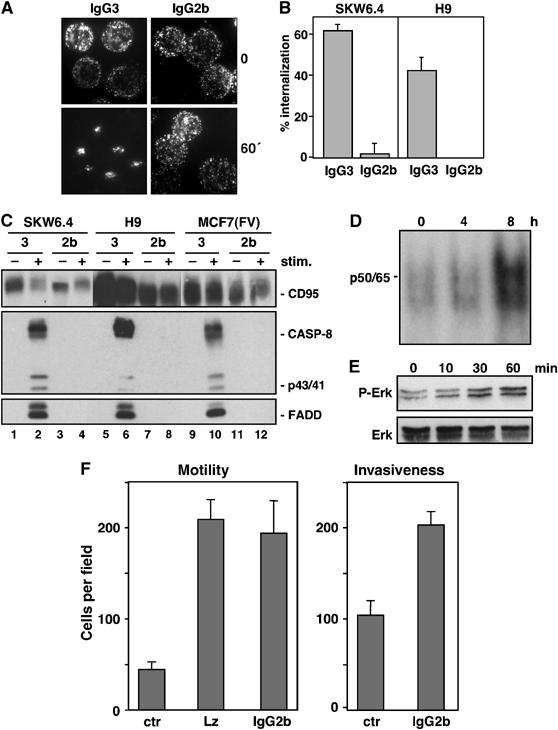
Activation of nonapoptotic signaling by anti-APO-1 IgG2b that does not induce CD95 internalization or apoptosis. (A) Effects of FITC-conjugated IgG3 (left two panels) and IgG2b (right two panels) anti-APO-1 mAbs on CD95 clustering in SKW6.4 cells was analyzed by fluorescence microscopy after 1 h of stimulation. (B) SKW6.4 cells were treated with either IgG3 or IgG2b anti-APO-1 mAbs for 1 h at 37°C. The number of cells with internalized CD95 following 1 h of Ab treatment was quantified. The experiment was performed in triplicates and is shown as the μ±s.d. (C) SKW6.4, H9 or MCF7(FV) cells were treated with IgG3 (lanes 1, 2, 5, 6, 9 and 10) or IgG2b (lanes 3, 4, 7, 8, 11 and 12) anti-APO-1 mAbs. Activated CD95 molecules were immunoprecipitated and analyzed by Western blotting for CD95 (C20), caspase-8 and FADD. (D) EMSA analysis of MCF7(FV) cells using a 32P-labeled oligonucleotide carrying NF-κB-binding sites stimulated with 1 μg/ml IgG2b anti-APO-1 for the indicated times. p50/p65 denotes the migration of the NF-κB heterodimer. (E) MCF7(FV) cells stimulated with 1 μg/ml IgG2b anti-APO-1 for the indicated times were analyzed for pErk and total Erk by Western blotting. (F) MCF7(FB) cells, treated with control (ctr), LzCD95L or IgG2b anti-APO-1 mAb, were analyzed using in vitro motility (left) or invasiveness (right) assays.
