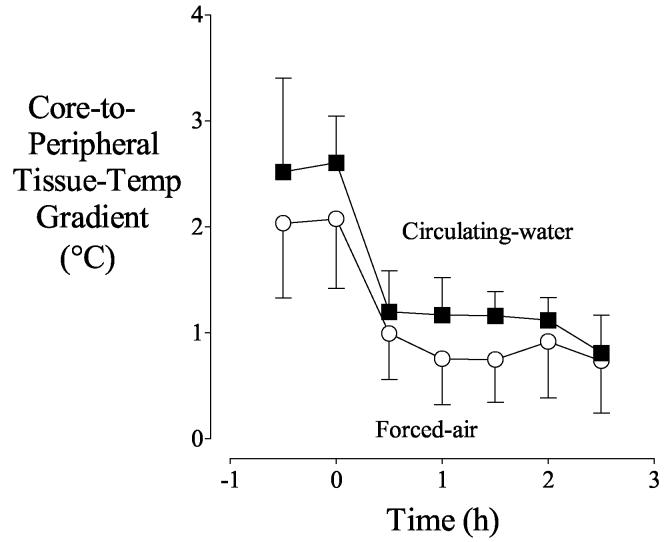
Fig. 5.
Core-to-peripheral tissue temperature gradient before and during warming. Average temperature of extremity tissues was considered peripheral temperature. Circulating-water or forced-air warming began at elapsed time zero. Results are presented as means with 95% confidence intervals. Although the gradient was slightly greater with circulating-water even before active warming, the shape of the curves was similar.