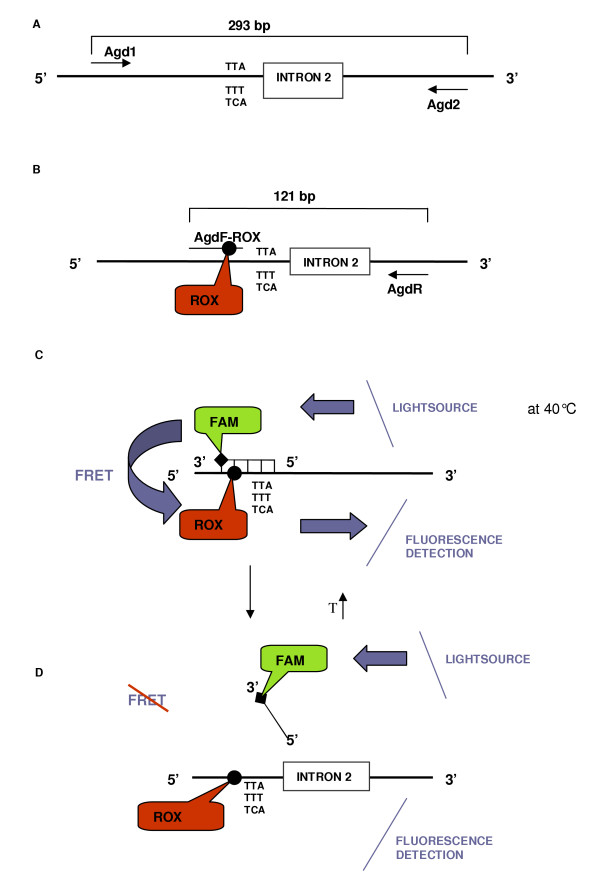
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the FRET/MCA, which allows the detection of both (L1014S and L1014F) kdr alleles in one assay. A. The primary PCR (primers Agd1-Agd2) results in amplification of a 293 bp fragment of the para-type sodium channel gene. B. During the secondary PCR, a 121 bp fragment is amplified and is labelled with ROX as the forward primer is extended. C. After amplification, the FAM-labelled probe hybridizes, and FRET starts to occur. The donor FAM-fluorophore is excited by incident light and because the ROX-acceptor is in close proximity, the excited state energy from FAM can be transferred. D. Melt curve analysis on the probe-amplicon hybrid. Progressive increase of temperature during melt curve analysis leads, at a specific temperature, to the dissociation of the probe from the amplicon. At this point, no FRET occurs and the ROX-fluorescence will decrease. During this MCA, the change in amount of fluorescence for each probe-template hybrid was plotted against the temperature and its negative derivative appeared as a positive peak.