Fig. 3.
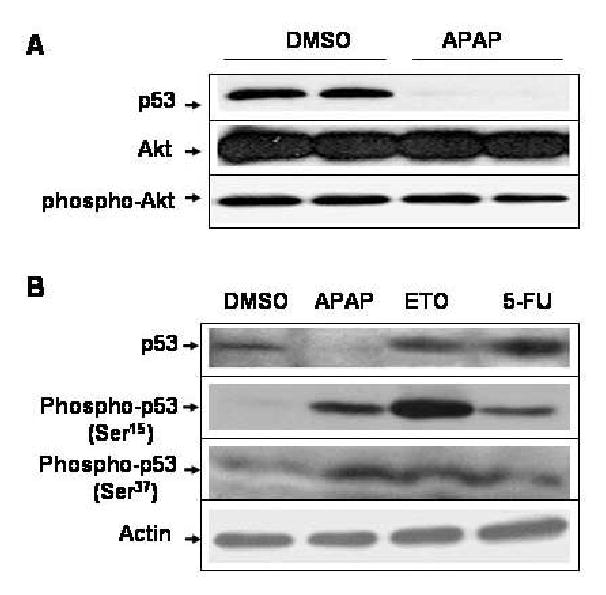
APAP-induced p53 reduction is independent from Akt or phospho-Akt and the phosphorylation status of p53 N-terminus. (A) Equal amounts of the soluble extracts (100 μg protein/well) from C6 cells treated with DMSO alone or 5 mM APAP for 24 h were separated on SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblot analysis using the specific antibody, as indicated: p53, Akt, and phospho-Akt, respectively. (B) C6 glioma cells were exposed to DMSO, 5 mM APAP, 10 μM etoposide (ETO), or 10 μM 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) for 24 h. Equal amounts of the soluble fraction from each treatment (100 μg protein/well) were separated on 10% SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblot analysis using the specific antibody against p53, phospho-p53 (Ser15 or Ser37), or actin.
