Fig. 5.
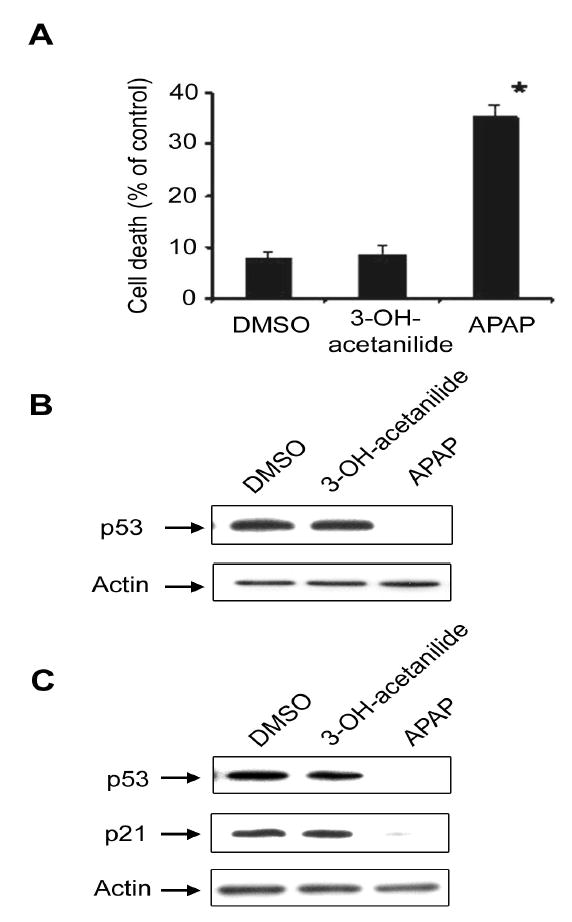
Differential effects of 3-hydroxyacetanilide and 4-hydroxyacetanilide on cell death rate and p53 reduction. (A) C6 glioma cells were treated with DMSO, 5 mM 3- hydroxyacetanilide, or 5 mM 4-hydroxyacetanilide (APAP) for 24 h. Cell death rate was then determined by MTT reduction. *, P < 0.01, significantly different from the cells treated with DMSO alone (vehicle control) or 3-hydroxyacetanilide. (B) Equal amounts of the soluble fraction (100 μg protein/well) were separated on 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gels followed by immunoblot analysis using the specific antibody against p53 (top) or actin (bottom). (C) LLC-PK1 cells were treated with DMSO, 5 mM 3-hydroxyacetanilide, or 5 mM APAP for 24 h before cell harvest. Equal amounts of the soluble fraction (20 μg/lane) were separated on 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gels and subjected to immunoblot analysis using the specific antibody against p53 (top), p21 (middle), or actin (bottom). This result represents a typical result of two independent experiments.
