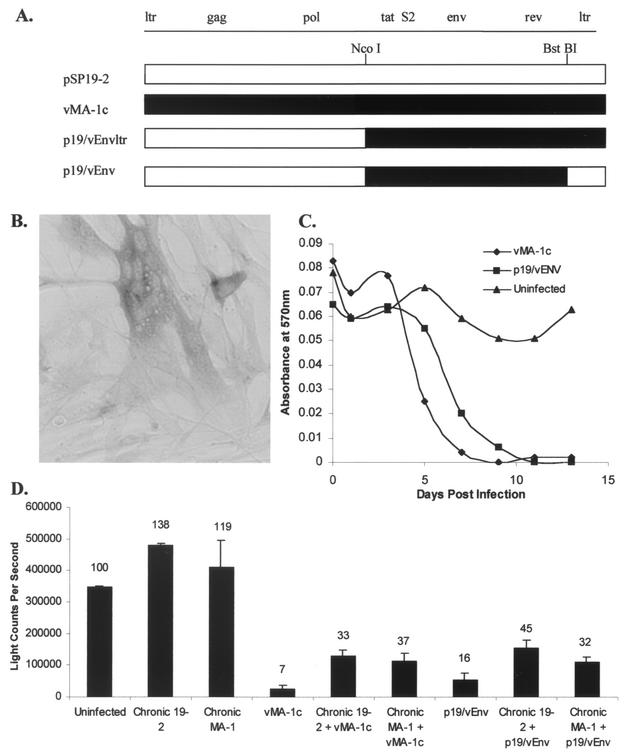
FIG. 8.
Chimeric EIAV infectious clones containing vMA-1c tat, S2, and env sequences resulted in increased syncytium formation within the ED cell culture, decreased cell numbers, and EIAV-infected ED cell superinfection. (A) Schematic diagrams of the chimeric clones p19/vEnvltr and p19/vEnv. (B) A photomicrograph of p19/vEnv fusogenic activity. Magnification, ×200. Syncytia were readily apparent in cultures infected with the chimeric virus 4 days postinfection. (C) Cell death resulted from p19/vEnv infection of ED cells. ED cells were infected at 24-h intervals with either vMA-1c or p19/vEnv. MTT assays were performed at the termination of the experiment as a measure of cell viability. Cell killing by p19/vEnv lagged behind vMA-1c killing by approximately 2 days. (D) Chronic EIAV infection does not protect ED cells from p19/vEnv-induced killing. ED cells or ED cells that were chronically infected with either MA-1 or pSP19-2 were infected with vMA-1c or p19/vEnv. At 8 days postinfection, cell viability was determined by ATPLite-M assay. The percentage of the uninfected-control value is shown above each bar.