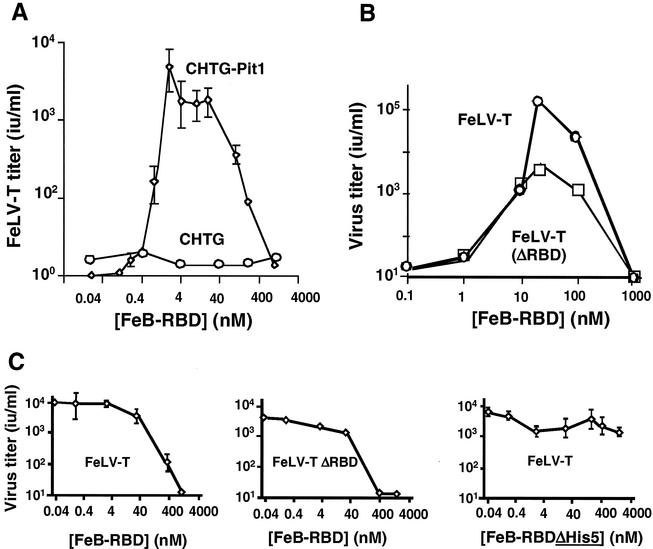
FIG. 7.
Virus and host requirements for FeLV-T infection. (A) FeB-RBD-activated FeLV-T infection is dependent on the Pit1 receptor. CHTG or CHTG-Pit1 cells that stably express human Pit1 receptor were exposed to serial dilutions of a retroviral vector derived from FeLV-T provirus, EECC(Ψ−), and encoding E. coli β-galactosidase. A specified concentration of purified FeB-RBD (0.01 to 1,000 nM) was added to the medium of each plate. After 4 h, medium containing virus and RBD was replaced with fresh medium. After an additional 48 h, cells expressing β-galactosidase were counted, and the virus titer (in international units/milliliter) was calculated by endpoint dilution. The data are the means ± 1 standard error of three independent experiments. (B) The presence of FeLV-T RBD is not required for FeB-RBD-dependent transactivation. The infectious titers of FeLV-T and FeLV-T (ΔRBD) in which RBD has been deleted from the virus envelope glycoprotein were measured as a function of FeB-RBD concentration on CHTG-Pit1 cells as described above. (C) The effect of FeB-RBD concentration on Fr-RBD-dependent FeLV-T infection of CHTG-mCAT1 cells stably expressing the Fr-RBD receptor, mCAT1, was measured. In each example, cells were exposed to virus and Fr-RBD (40 nM) and the indicated concentration of FeB-RBD (left and center panels, 0.04 to 1,000 nM) or FeB-RBD (ΔHis5) in which the His5 residue was deleted (right panel, 0.04 to 4,000 nM). Under these conditions, the infectious titers of FeLV-T (left panel), FeLV-T (ΔRBD) (center panel), and FeLV-T (right panel) were measured as in panels A and B.